Fig 3.
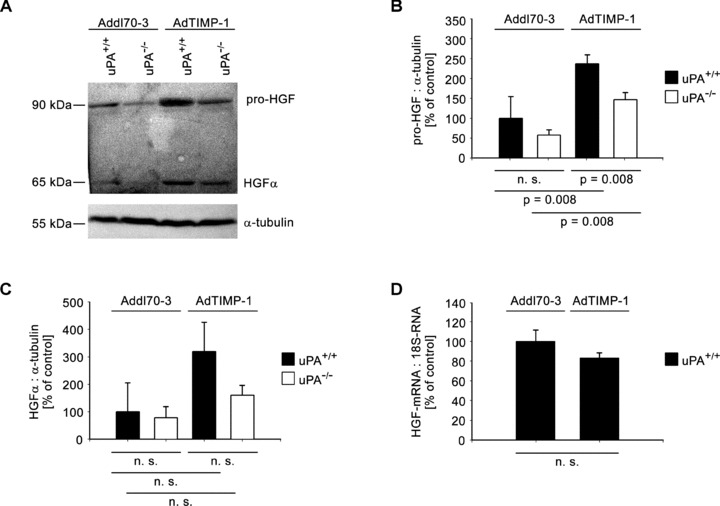
(A) Representative Western blot of pro-HGF and its activated form (HGF-α) in liver protein of META/Bomnu/nu mice (uPA+/+ and uPA−/−, respectively), transduced by either AdTIMP-1 or Addl70–3 adenoviruses. (B and C) Densitometries of all performed Western blots revealed increase of HGF protein levels and its activation in livers with elevated TIMP-1. Loss of host uPA reduced the amounts both of latent and activated HGF. Columns: Mean intensities of either pro-HGF (B) or HGF-a bands (C) versusα-tubulin band intensities. The mean of the reference group Addl70–3/uPA+/+ was set as 100%, respectively. Bars: S.E. n= 5 mice. (B) Addl70–3/uPA+/+: 100.0%± 24.5%; Addl70–3/uPA−/−: 58.0%± 5.8%; AdTIMP-1/uPA+/+: 237.3%± 9.8%; AdTIMP-1/uPA−/−: 146.5%± 8.0%. (C) Addl70–3/uPA+/+: 100.0%± 52.9%; Addl70–3/uPA−/−: 78.6%± 20.1%; AdTIMP-1/uPA+/+: 319.2%± 53.2%; AdTIMP-1/uPA−/−: 159.8%± 18.1%. (D) qRT-PCR of HGF mRNA in livers of META/Bomnu/nu wild-type mice. Columns: Mean amount of the HGF mRNA versus 18S-RNA. The mean of the reference group Addl70–3/uPA+/+ was set as 100%. Bars: S.E. n= 3 mice. Addl70–3/uPA+/+ 100.0%± 11.8%; AdTIMP-1/uPA+/+ 83.0 ± 5.5%.
