Fig 1.
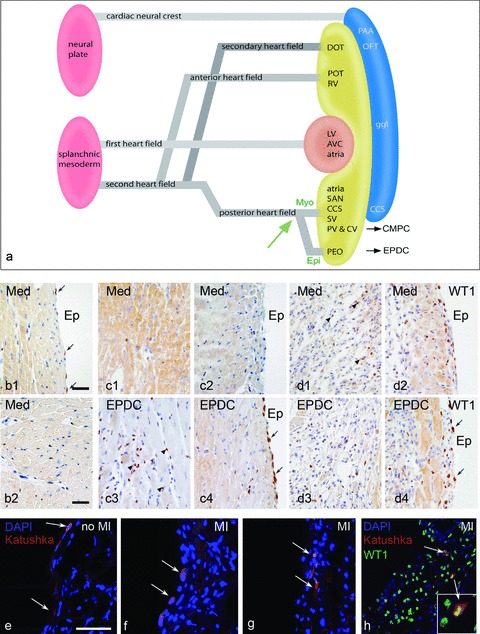
(a) Schematic representation of the first and second heart field contribution to the developing heart. The venous pole (posterior heart field) is essential as source of EPDCs and CMPCs, a differentiation in a myocardial and epicardial lineage from the progenitor population is guided by the balance of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) and fibroblastic growth factor 2 (Fgf2) [27]. (b) Expression of WT1 in the surface epicardium (b1) and intramyocardially (b2) in a control adult mouse heart is very limited (arrows). Two days after MI, with injection of medium, this is not substantially altered (c1,2) except for the cases with injection of EPDCs (c3,4), where both the surface epicardium and the interstitial fibroblasts show marked WT1 expression. At day 4 after MI this phenomenon is also present in the medium injected heart (d1,2) and maintained in the heart after EPDC transplantation (d3,4). Injection of the lentiviral Katushka construct into the epicardial cavity showed, after 4 days survival, staining of the squamous surface epicardium in the control heart (e, arrows). After MI the surface epicardium becomes cuboid (f, arrows) indicative of activation and cells can be traced intramyocardially (g, arrows) after EMT, which is supported by double staining of Katushka and WT1 (h). Scale bars b1–d4:30 μm, e–h:50 μm.
