Fig 4.
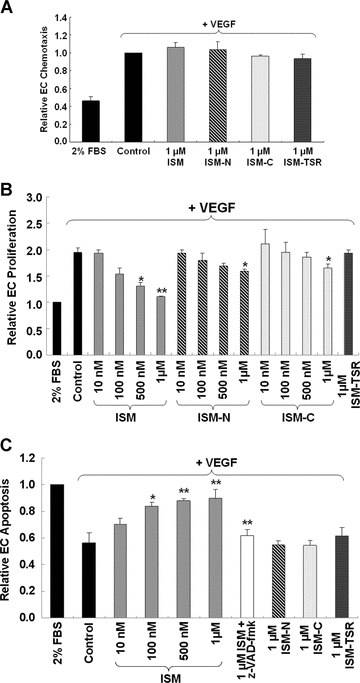
The effects of ISM and its various domains on various aspects of in vitro angiogenesis. (A) ISM does not influence VEGF-induced chemotactic EC migration. The concentrations of ISM, ISM-N, ISM-C and ISM-TSR tested were from 1 nM to 1 μM. Only results of 1 μM were shown. (B) ISM suppressed VEGF-induced EC proliferation. Both ISM-N and ISM-C have a weaker activity comparing to ISM, whereas ISM-TSR is not active. Only 1 μM result was shown for ISM-TSR. (C) ISM induced EC apoptosis in the presence of VEGF in a dose-dependent manner. The ISM-induced EC apop-tosis was abolished when pan-caspase inhibitor z-VAD-fmk was added. None of the ISM truncated fragments (at concentrations from 10 nM to 1μM) showed such activity (only 1 μM result was shown) *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, n= 4. VEGF used was 15 ng/ml in all experiments.
