Fig. 2.
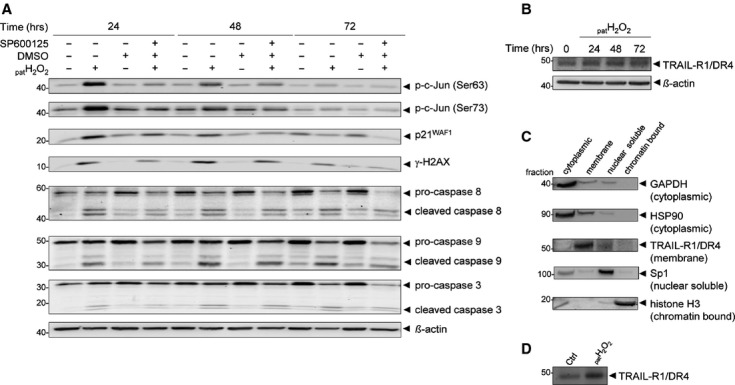
Identification of cellular JNK-regulated proteins in H2O2-exposed HCEC. (A) Immunoblot analysis following JNK inhibition by the JNK inhibitor SP600125 revealed p21WAF1, γ-H2AX, as well as caspases 3, 8 and 9 as cellular JNK-regulated proteins. The effective inhibition of JNK was ensured through missing phosphorylation of the transcription factor c-jun at serine residues 63 and 73. (B) Immunoblot analysis showed an overexpression of the death receptor TRAIL-R1/DR4 after H2O2. (C) Immunoblot analysis of subcellular fractionated cellular proteins of H2O2-treated HCEC. Each extract was analysed using specific antibodies against proteins from various cellular compartments, including cytoplasmic (GAPDH, HSP90), plasma membrane (TRAIL-R1/DR4), nuclear soluble (Sp1) and chromatin-bound (histone 3). (D) Analysis of the membrane extracts of HCEC and H2O2-exposed HCEC by immunoblotting showed accumulation of the TRAIL-R1/DR4 in H2O2-exposed cells.
