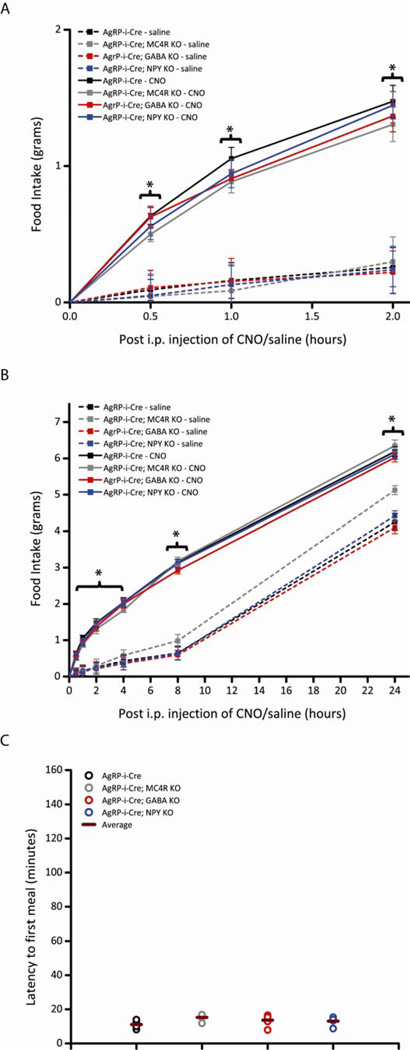
Figure 2.
Acute pharmaco-genetic activation of AgRP neurons in mice without release of GABA, NPY or AgRP signaling via MC4Rs, individually, display intact DREADD-mediated increases in food intake (Pooled data across multiple trials). All mice in these studies were bilaterally injected with AAV8-DIO-hM3Dq-mCherry in the ARC. (A-C) Activation of AgRP neurons increases comparable levels of food intake and latency to first meal in AgRP-ires-Cre mice (black line), AgRP-ires-Cre; Mc4r−/− KO mice (grey line), AgRP-ires-Cre; Vgatflox/flox KO mice (red line) and AgRP-ires-Cre; Npy−/− KO mice (blue line). CNO (solid line; 0.3 mg/kg of body weight, i.p.) or saline (dotted line) was injected 3 hr after the start of the “lights on” cycle and food intake was assessed (A) 1-, 2-, (B) 4-, 8- and 24- hr post-injection (PI) over three trials of each treatment. Data shown is from male mice (Error bars indicate mean +/− SEM, n=8 AgRP-ires-Cre mice; n=5 AgRP-ires-Cre; Mc4r−/− mice; n=7 AgRP-ires-Cre; Vgatflox/flox mice; n=8 AgRP-ires-Cre; Npy−/− mice; *P<0.05 CNO groups versus all saline groups; #P<0.05 AgRP-ires-Cre; Mc4r−/− saline group versus all other saline groups). (C) Latency to first meal following acute pharmaco-genetic activation of AgRP neurons. Each circle represents the average of two trials for each mouse; horizontal bar represents average of all mice. Data shown is from male mice (mean ± SEM, n=7 AgRP-ires-Cre mice; n=5 AgRP-ires-Cre; Mc4r−/− mice; n=5 AgRP-ires-Cre; Vgatflox/flox mice; n=5 AgRP-ires-Cre; Npy−/− KO mice). See also Figure S2 and Table S1.