Fig 1.
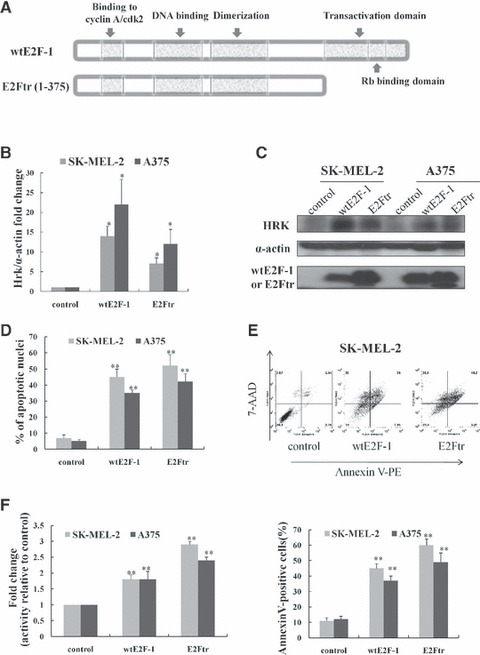
Overexpression of wtE2F-1 and E2Ftr leads to increased Hrk expression and apoptosis in melanoma cells. (A) Schematic representation of wtE2F-1 and E2Ftr domain structure. Two melanoma cell lines (SK-MEL-2 and A375) were infected with Ad-LacZ (control vector), Ad-wtE2F-1 or Ad-E2Ftr at MOI 100. After 24 hrs of infection, real-time RT-PCR (B) and Western blot analysis (C) were performed as described in Materials and methods. (B) RT-PCR results are expressed as Hrk fold increase relative to control vector-infected cells adjusted for α-actin as an internal control. Each experiment is a representation of three independent experiments performed in duplicate (bars: mean ± S.D.; *P < 0.05 compared with control; n = 3). (C) Cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis using HRK, wtE2F-1 or E2Ftr and α-actin antibody. (D) After 48 hrs of infection, the percentage of apoptotic cells showing typical apoptotic nuclei by Hoechst 33258 staining was counted under a fluorescence microscope. The percentage of apoptotic cells (annexin V-PE+ cells) were also determined by flow cytometry analysis (E) after 48 hrs of infection, as described in Materials and methods. (F) After 48 hrs of designated infection, the OD405 values of the cell lysates were measured as caspase-9 activity. The results were expressed as the fold change in treated cells over that of the control cells. Values represent mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments (bars: mean ± S.D.; **P < 0.01 compared with control; n = 3).
