Fig 5.
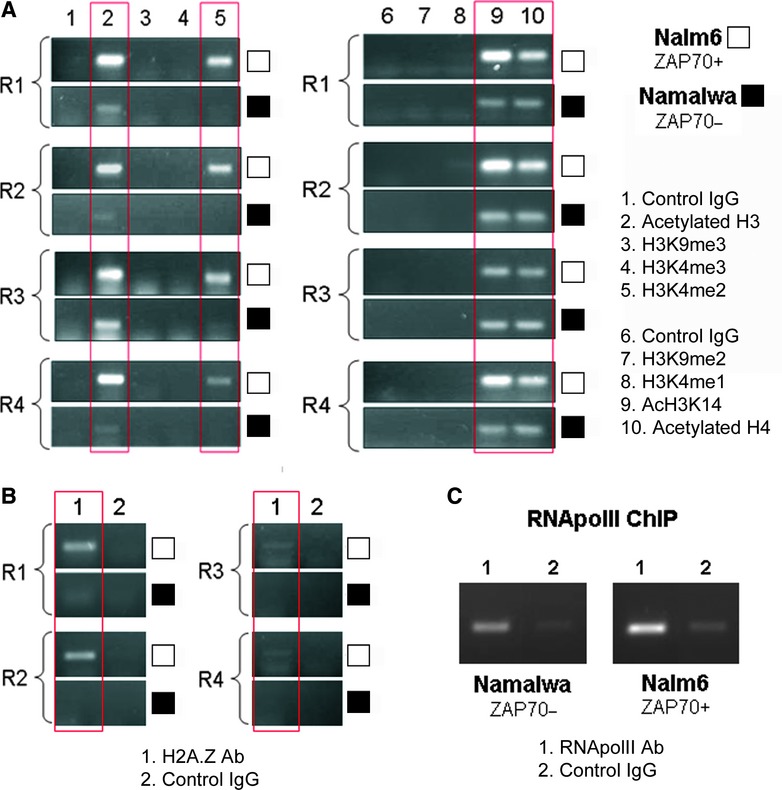
Significant differences in histone modification associated with ZAP70 promoter in ZAP70 expressing versus the non-expressing cell line. (A) 100 μg of native chromatin obtained from Nalm6 or Namalwa cell lines was incubated with 10 μg of antibodies raised against acetylated H3, H3K9me3, H3K4me3, H3K4me2, H3K9me2, H3K4me1, acetylated H3K14 and acetylated H4 or control antibody; ChIP assay was carried out and R1 to R4 ZAP70 promoter fragments were amplified. Gels shown are representative of four replicate experiments. White blocks depict Nalm6 ZAP70+ve cell samples; black blocks show Namalwa ZAP70−ve samples. (B) 100 μg of native chromatin obtained from Nalm6 or Namalwa cell lines was incubated with 10 μg of anti H2A.Z or control antibody; ChIP assay was carried out and R1 to R4 ZAP70 promoter fragments were amplified. Gels shown are representative of three replicate experiments. White blocks depict Nalm6 ZAP70+ve cell samples; black blocks show Namalwa ZAP70−ve samples. (C) 100 μg of cross-linked chromatin obtained from Nalm6 or Namalwa cell lines was incubated with 10 μg of anti RNApol II or control antibody; ChIP assay was carried out and R4 ZAP70 promoter fragment was amplified. Gels shown are representative of three replicate experiments.
