Fig 2.
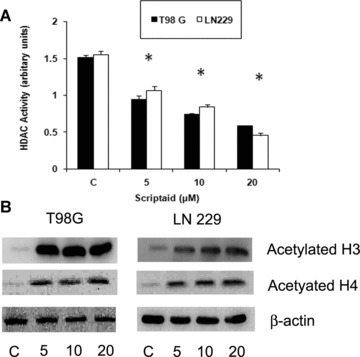
Scriptaid decreases HDAC activity and increases histone acetylation of glioma cells. (A) Scriptaid treatment decreases HDAC activity in glioma cells. HDAC activity of scriptaid-treated LN229 and T98G cells was performed using HDAC activity assay kit according to manufacturer's instruction. A decrease in HDAC activity in LN229 and T98G cells upon exposure to increasing dose of scriptaid was observed. Values represent the means ± SEM from three independent experiments. *Significant decrease from control (P≤ 0.05). (B) Scriptaid induces H3 and H4 hyperacetylation in glioma cells. Western blot analysis was performed on nuclear extracts obtained from LN229 and T98G cells treated with scriptaid. An increase in H3 and H4 acetylation was observed upon exposure of glioma cells to increasing concentration of scriptaid. A representative blot is shown from three independent experiments with identical results. Blots were reprobed for β-actin to establish equivalent loading.
