Fig 5.
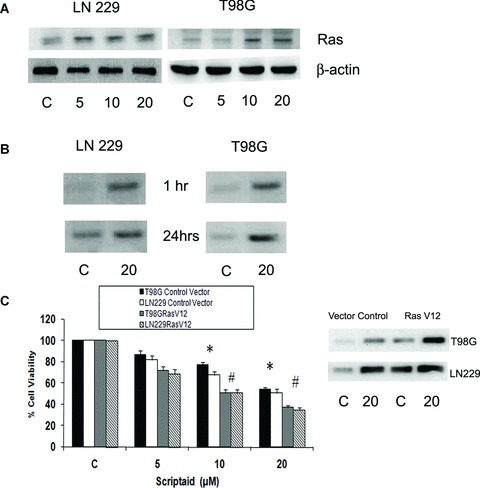
Scriptaid increases the expression and activity of Ras in glioma cells. (A) Scriptaid increases Ras expression in glioma cells in a dose-dependent manner. LN229 and T98G cells were treated with different concentration of scriptaid, and Ras level was determined by Western blot analysis. A representative blot is shown from three independent experiments with identical results. Blots were reprobed for β-actin to establish equivalent loading. (B) Effects of scriptaid on the levels of GTP-bound Ras. The levels of Ras-GTP in protein extracts of control and scriptaidtreated LN229 and T98G cells were determined by the ability of Ras-GTP to bind to a specific protein domain of Raf in the form of a GST-fusion protein. An increase in Ras activity was observed in glioma cells treated with increasing concentration of scriptaid both at 1 and 24 hrs post-treatment, as compared to the control. The figure is representative from three independent experiments with identical results. (C) Scriptaidinduced cell death is dramatically increased in the presence of constitutive Ras. Glioma cells transfected with constitutive active Ras (RasV12) were treated with scriptaid for 24 hrs and cell viability was determined by MTS assay. Ras activity in cells transfected with RasV12 or control vector in the presence or absence of scriptaid. The graph represents the percentage of viable cells as determined by MTS assay, observed when RasV12-transfected or untransfected glioma cells were treated in the presence and absence of scriptaid for 24 hrs. Values represent the means ± SEM from three independent experiments. *Significant decrease from control (P≤ 0.05); #significant change from scriptaid-treated cells (P≤ 0.05).
