3.
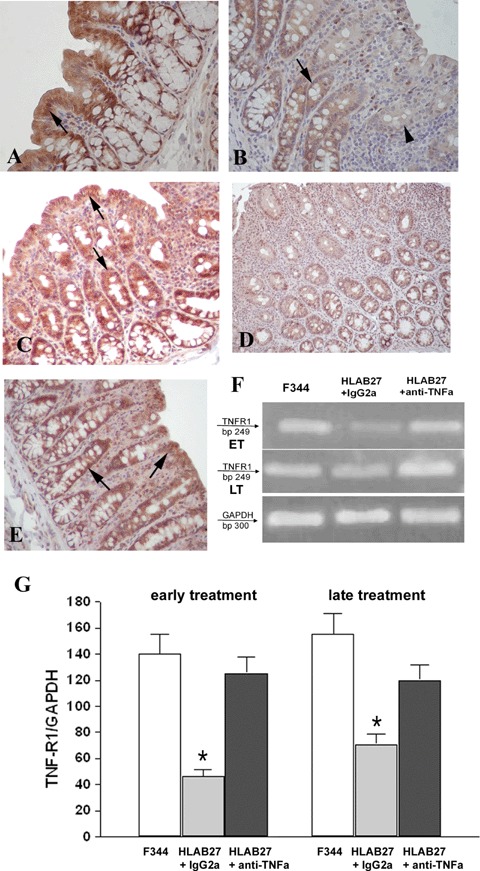
Detection of TNFα receptor 1 (TNF-R1) in colonic mucosal tissue. (A) Positive colonic intestinal epithelial cells (IEC) for TNF-R1 in non-transgenic F344 rats (arrow). (B) IgG2 a, k-treated B27TR colon with weakly stained (arrow) or negative (arrowhead) IEC. (C) The early treatment with anti-TNFα mAb preserves the expression of TNF-R1 in IEC (arrows). (D) 27-week-old IgG2a,k-treated B27TR showed negative immunoreactivity for TNF-R1 in IEC. (E) The late treatment with anti-TNFα mAb restored the expression of TNF-R1 in IEC (arrows). Brown colour: DAB immunohistochemical developing; Red colour: AEC immunohistochemical developing; Blue colour: haematoxylin counterstain. Original magnification ×40. (F, G) RT-PCR results for TNF-R1 are shown. TNF-R1 was well expressed in non-transgenic F344 rats, whereas it was down-regulated in IgG2a, k-treated B27TR, both at 18 and 27 weeks. Early treatment with anti-TNFα mAb maintained the expression of TNF-R1 mRNA at control levels. The late treatment increased the mRNA to control levels. Data are representative of at least three separate experiments. *P < 0.05 IgG2a,k-treated B27TR versus F344 and anti-TNFα-treated B27TR. ET: early treatment; LT: late treatment.
