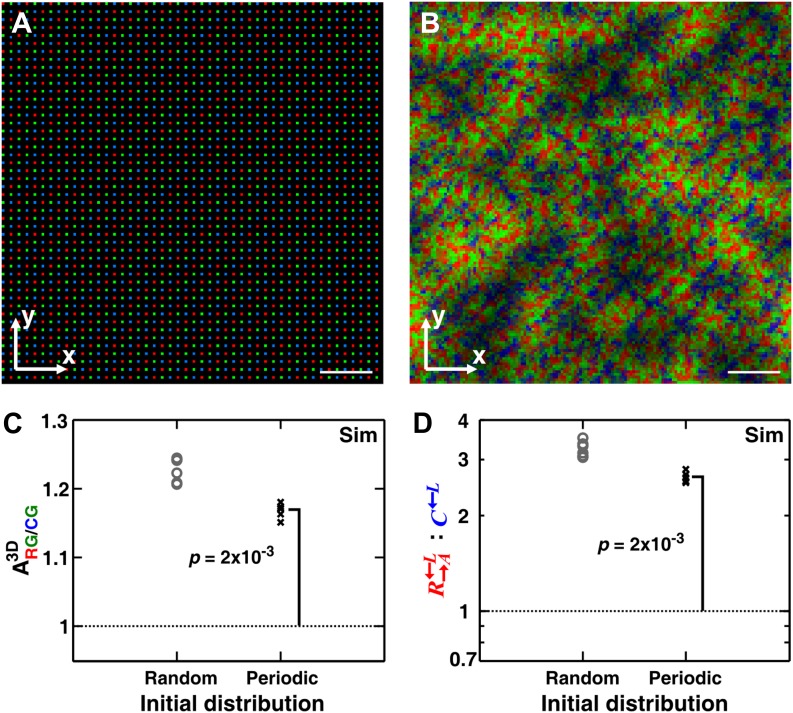
Figure 5. Heterogeneity in the initial spatial distribution of cells facilitates but is not required for cheater isolation.
Starting from a symmetric and periodic distribution in which all cooperators and cheaters had an equal access to the partner (A), heterotypic cooperators self-organized (B and C) and were favored (D). (B–D) corresponded to generation 6. Break of symmetry from the initial symmetric spatial distribution can be due to stochastic effects such as differences in the initial amounts of metabolites cells possessed, death of cells, or the random direction of cell division. Compared to a random initial distribution, communities with a periodic initial distribution showed smaller mean ; nonetheless, significantly exceeded 1 (Wilcoxon signed rank test). In these simulations, the growth rate advantage of over was assumed to be 10% at all concentrations of lysine. The communities were initiated at 4400 total cells/mm2. Scale bar: 100 μm. In simulated top-views, higher color intensity indicates a greater number of cells of the corresponding color stacked at that position. Sim: simulation.