Fig 2.
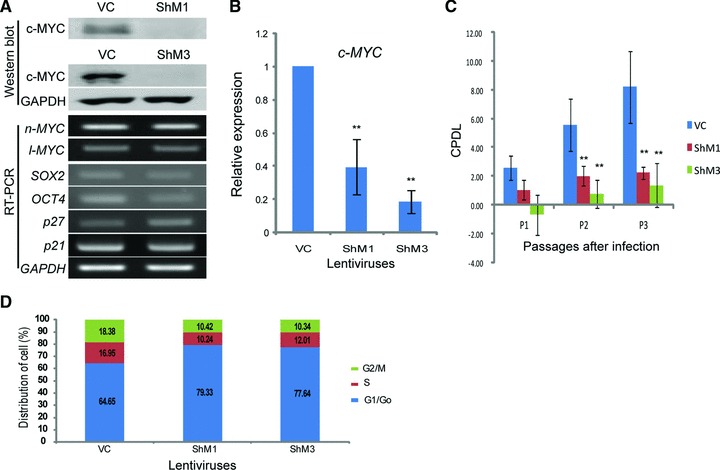
The knockdown of c-MYC results in growth retardation. (A) RNA and protein expression after c-MYC-inhibiting lentivirus infection. Two constructs of c-MYC-inhibiting lentivirus, ShM1 and ShM3, show effective inhibition in hUCB-MSCs. (B) Real-time RT-PCR after c-MYC inhibition in hUCB-MSCs. The expression of c-MYC is decreased by approximately 60% (ShM1) and 80% (ShM3) of the vector control-infected hUCB-MSCs. (C) Cell proliferation is measured with CPDL. c-MYC knocked-down hUCB-MSCs show severe growth retardation. (D) FACS analysis after c-MYC knockdown in hUCB-MSCs. G0/G1 cells are increased in c-MYC knocked-down hUCB-MSCs compared to those of the vehicle control-infected hUCB-MSCs. VC: vehicle control infected hUCB-MSCs. **P < 0.01.
