Fig 2.
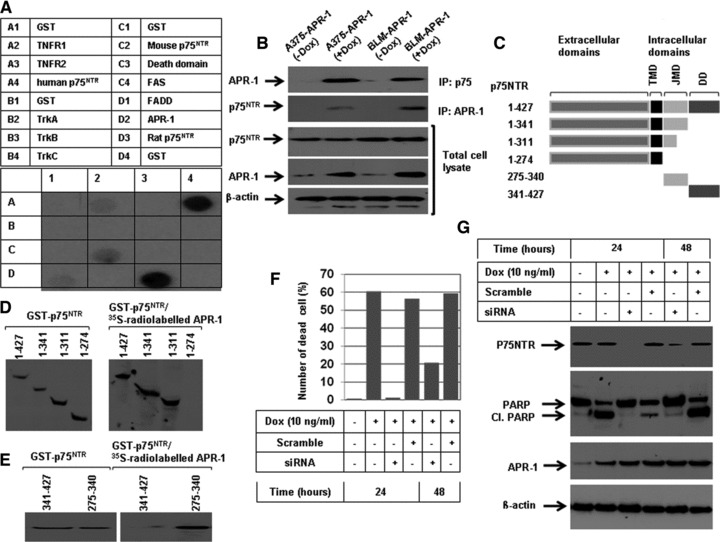
(A) Dot blots analysis of the interaction of APR-1 protein with TNFR1 human p75NTR, mouse p75NTR, FADD and rat p75NTR. A total of 5 μg of glutathione S-transferase (GST)-TNFR1 (100.0 pmol), TNFR2 (111.0 pmol), human p75NTR (106.4 pmol), mouse p75NTR (106 pmol), FADD (92.6 pmol), TrKA (113.6 pmol), TrKB (113.6 pmol), TrKC (113.6 pmol), Fas 142.8 pmol), death domain (142.8 pmol), APR-1 (100 pmol), rat p75NTR (106 pmol) or GST (192.0 pmol) were diluted in PBS and blotted onto nitrocellulose membrane and subsequently incubated overnight with in vitro transcribed and translated [35S] APR-1 protein. (B) Interaction of APR-1 with P75NTR. The total cell lysates prepared from A375-APR-1 and BLM-APR-1 before and after the induction of APR-1 protein were subjected for either electrophoresis (for the detection of APR-1 and P75NTR) or for co-immunoprecipitation (IP) with either anti-P75NTR antibody or with anti-APR-1 antibody. Western blotting of IP: p75NTR for APR-1 revealed the interaction of APR-1 to P75NTR, whereas Western blotting of IP: APR-1 for P75NTR revealed the interaction of P75NTR to APR-1. β-actin was used as internal control for loading and transfer. (C) Schematic diagram of the extracellular and intracellular domains of p75NTR. Transmembrane domain, JMD and death domain. (D) GST-P75NTR recombinant proteins 1–427aa (106.4 pmol), 1–341aa (135.1 pmol), 1–311aa (147 pmol), 1–274 aa (166 pmol), 275–340aa (694.3) and 341–427aa (526.2 pmol), were separated by SDS-PAGE, and blotted on PVDF membrane and probed with in vitro transcribed and translated [35S] APR-1. The interaction of APR-1 with the P75NTR domains was detected by exposing the membrane to X-ray films. The coomassie-stained gel shows the amount and the position of P75NTR recombinant proteins (left panel). (E) GST-JMD and death domain of P75NTR were separated by SDS-PAGE, and blotted on PVDF membrane and probed with in vitro transcribed and translated [35S] APR-1. The interaction of APR-1 with both domains was detected by exposing the membrane to X-ray films. The coomassie-stained gel shows the amount of both JMD and death domains (left panel). (F) Western blot analysis demonstrates the expression of APR-1 by the addition of Dox to the culture medium of BLM-APR- 1, the knockdown of p75NTR by its specific siRNA and the suppression of APR-1-induced cleavage of PARP by the p75NTR siRNA. β-actin was used as internal control for loading and transfer. (G) Analysis of cell viability by counting using trypan blue staining. Rescue of APR-1-induced reduction of cell viability by the knockdown of p75NTR by siRNA for 24 or 48 hrs. Data are mean of three experiments performed separately.
