Fig 3.
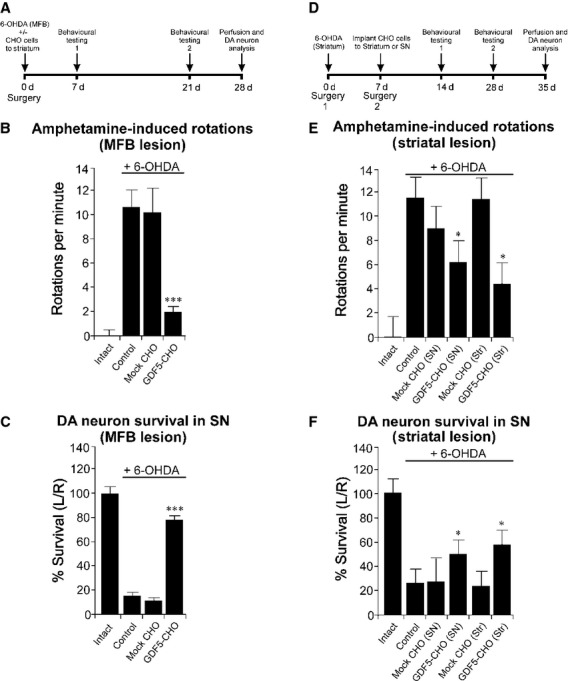
Neuroprotective and neurorestorative effects of GDF5-CHO cells in two adult rat models of PD. (A) Outline of experiment to analyse the neuroprotective effect of GDF5-CHO cells in the 6-OHDA MFB lesion model of PD. (B) Amphetamine-induced rotational rates at 21 days post-surgery for each treatment group (n = 5 per group). (C) Survival of dopaminergic neurons in the SN at 28 days post-surgery expressed as the number of TH-positive neurons in the left SN as a percentage of those in the right. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. ***P < 0.001 compared with control (lesion only) and mock-CHO groups, anova with post-hoc Tukey's test. (D) Outline of experiment to analyse the neurorestorative effect of GDF5-CHO cells in the 6-OHDA striatal lesion model of PD. (E) Amphetamine-induced rotational rates at 28 days post-surgery for each treatment group (n = 5 per group). (F) Survival of dopaminergic neurons in the SN at 35 days post-surgery, expressed as the number of TH-positive neurons in the left SN as a percentage of those in the right. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 compared with control (lesion only), mock-CHO (SN) and mock-CHO (striatum) groups; anova with post-hoc Tukey's test.
