Fig 1.
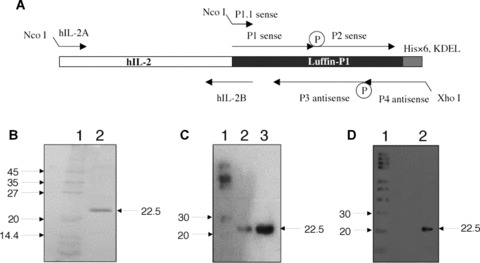
Expression of hIL-2-Luffin P1 immunotoxin. (A) Schematic illustration of gene synthesis for Luffin P1 and hIL-2-Luffin P1. Synthetic oligos P1, P2, P3 and P4 were annealed, ligated and extended to form the full-length Luffin P1 gene, which was further amplified with P1.1 and P4. The hIL-2 gene was amplified with primers hIL-2A and hIL-2B, and the resulting fragment was fused with Luffin P1 by overlapping PCR with hIL-2A and P4 primers. Both genes were cloned into the bacterial expression vector pET-20b(+) at NcoI and XhoI sites. P represents phosphate groups at the 5′ end of oligos required for the ligation reaction. The His×6 tag and KDEL sequence are indicated. (B) SDS-PAGE detection of hIL-2-Luffin P1 purified by His-Bind resin. A single 22.5 kD band of hIL-2-Luffin P1 in Lane 2 can be visualized. Molecular weight markers in Lane 1 were denoted in kD on the left. (C) Western blot detection of purified hIL-2-Luffin P1 (both Lane 2 and Lane 3 on different loading) with anti-His tag antibody. Positive bands at 22.5 kD were shown by arrow. Lane 1 is the molecular weight marker. A similar Western blot with anti-hIL-2 antibody was shown in (D).
