Fig 2.
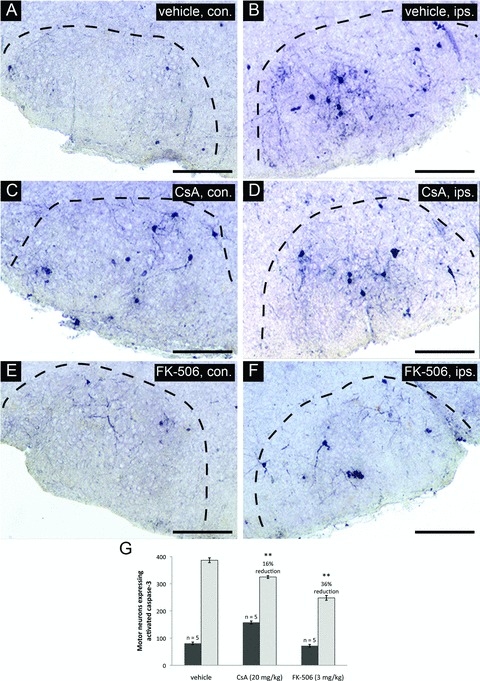
CsA or FK-506 treatment reduces levels of activated caspase-3 in facial motor neurons following axotomy. Coronal cross-sections through the facial nucleus were examined for activated caspase-3 at 20 hrs following axotomy for drug treatment groups and vehicle-treated controls. (A), (C) and (E) show sections through uninjured facial nuclei (contralateral – con.). (B), (D) and (F) show sections through injured facial nuclei (ipsilateral – ips.). Scale bars represent a distance of 250 μm. (G) Stereological counts of activated caspase-3 positive neurons through the facial nucleus show that both CsA and FK-506 treatments significantly reduced the number of motor neurons positive for activated caspase-3 compared to vehicle treatment (** indicates statistical significance at P < 0.01 between treatment groups and vehicle controls). Notably, CsA treatment was observed to increase the total number of motor neurons with activated caspase-3 in the uninjured facial nuclei compared to vehicle controls (** indicates statistical significance at P < 0.01 between CsA and vehicle treatments) whereas FK-506 did not appear to have any effects on uninjured facial motor neurons.
