1.
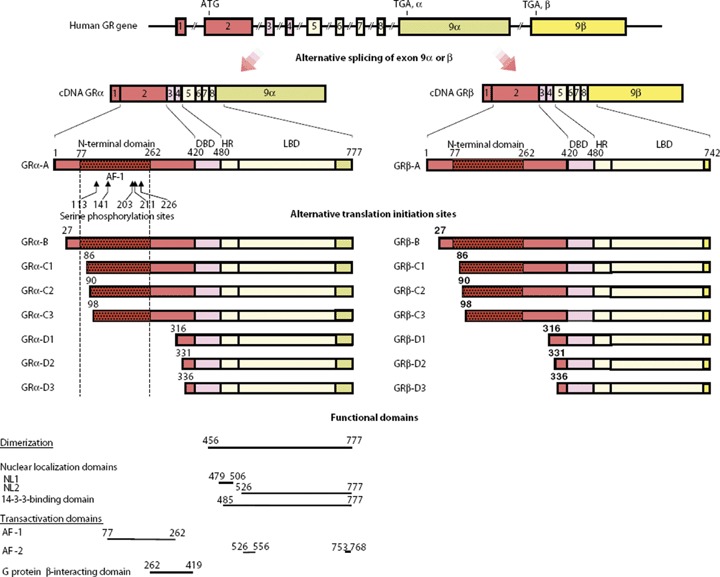
Genomic and complementary DNA, protein structures and functional domains of human GR isoforms. The human GR gene consists of 10 exons. Exon 1 is an untranslated region; exon 2 encodes the N-terminal ‘immunogenic’ domain; exons 3 and 4 encode the DNA-binding domain;and exons 5 through 9 encode the hinge region and the LBD. The GR gene contains two terminal exon 9s (9α and 9β), which are alternatively spliced to produce the classic GR-α (GRα-A) and the non-ligand-binding GRβ-A, which exerts dominant negative effects upon GR-α (GRα-A). C-terminal domains colored as light green and yellow in GRαs and GR-βs show unique portions of their amino acid sequences. GR-α N-terminal translational isoforms expressed from a single GR-α transcript are shown in the middle of the figure. The GR-β transcript may also produce similar N-terminal isoforms from the same start sites as GR-α. AF-1 and -2, activation function 1 and 2; DBD, DNA-binding domain; HR, hinge region; LBD, ligand-binding domain; NL1 and 2, nuclear translocation signal 1 and 2. ‘From G. P. Chrousos, T. Kino. Intracellular glucocorticoid signalling: A formerly simple system turns stochastic. Sci. STKE 2005, pe48. Reprinted with permission from AAAS’.
