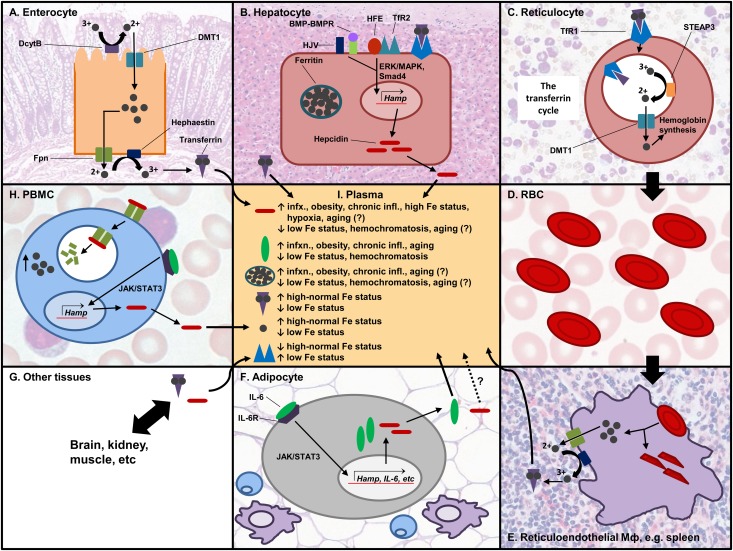
FIGURE 1.
Post-translational regulation of iron homeostasis. Iron is absorbed through the enterocyte (A). It is first reduced by DcytB and transported by DMT1 into the cell, and it is either stored or exported from the cell by the action of hephaestin and ferroportin. Two iron atoms bind transferrin, which transports iron to target tissues. (B) Iron can be stored in hepatocytes in the storage protein ferritin. The liver is the main producer of hepcidin, and its expression can be induced by HJV/BMP-BMP receptor, or by TfR2/HFE through the Smad4 or ERK/MAPK pathways, respectively. (C) In the bone marrow, reticulocytes take in transferrin-bound iron to make Hb. The TfR/transferrin-iron complex is internalized by endocytosis. Acidification of the endosome induces the release of iron from transferrin. Iron is reduced and exported into the cytoplasm and used for Hb synthesis in the mitochondria. TfR and transferrin are recycled back to the cell membrane. (D) RBCs transport the synthesized Hb and are involved in oxygen and CO2 exchange with different tissues. (E) Effete RBCs are recycled via the reticuloendothelial system. Macrophages phagocytose the RBCs and recycle the iron. (F) AT secretes adipokines, including pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 that induce hepcidin expression via the JAK/STAT3 pathway. It is not confirmed whether hepcidin made in AT goes into circulation. (G) Transferrin and hepcidin go to different tissues in the body that utilize iron. (H) PBMCs are one of the cell types that express ferroportin. Hepcidin binds ferroportin and induces its internalization and degradation, increasing the intracellular iron pool. (I) Different proteins are found in circulation, and their levels affect or are affected by iron status. AT, adipose tissue; DcytB, duodenal cytochrome B; DMT1, divalent metal transporter 1; Fpn, ferroportin; Hamp, hepcidin gene; Hb, hemoglobin; HJV, hemojuvelin; IL-6, interleukin 6; JAK/STAT3, Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; PBMCs, peripheral blood mononuclear cells; RBCs, red blood cells; STEAP3, six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 3; TfR, transferrin receptor. Source for histology images: Wheater's functional histology: a text and colour atlas (112).