Figure 2.
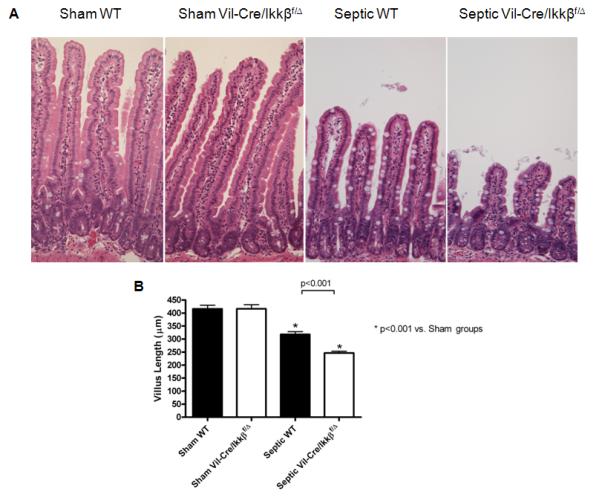
Sepsis-induced villus atrophy is exacerbated in mice lacking functional enterocyte NF-kB. Intestinal morphology (A) was evaluated in hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained intestinal sections. Septic WT mice had markedly shorter villi than sham mice. Villi were even shorter in septic Vil-Cre/Ikkßf/Δ mice. Magnification x20. Villus length was quantified in sections of jejunum (B). Septic WT mice had significantly increased villus atrophy, which was exacerbated in the absence of functional enterocyte NF-kB (septic Vil-Cre/Ikkßf/Δ mice). n=12-13/group.
