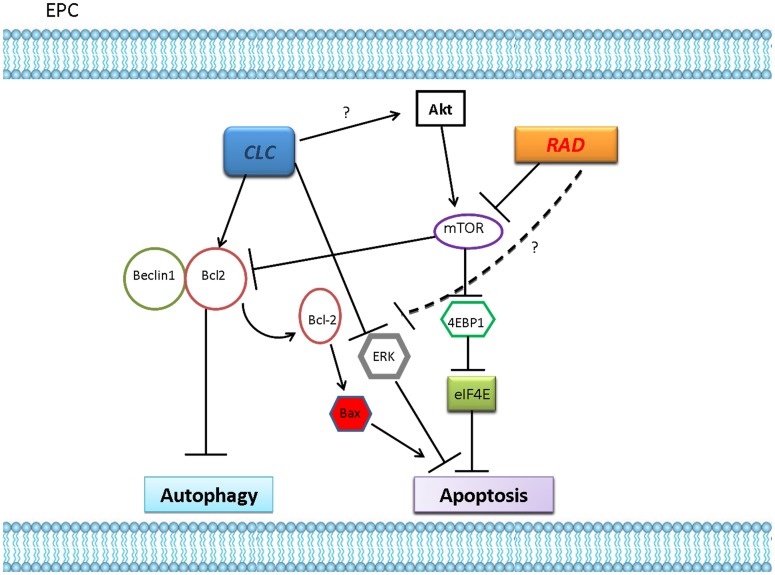
Figure 8. Scheme of the effects induced by RAD/CLC interaction.
(Right part) RAD inhibits mTOR and the downstream anti-apoptotic eIF4E-dependent pathway and, at the same time, causes inactivation of the beclin-1/bcl-2 complex formation inhibiting autophagy. Moreover, RAD induces a slight decrease of the activity of the survival enzymes Erk-1 and 2. (Left part) CLC increases the formation of the beclin-1/bcl-2 complexes thus inhibiting autophagy and, at the same time, induces a slight decrease of the Erk-1/2 activity and increases Akt activity. On these bases, the addition of CLC before RAD to EPCs inhibits autophagy occurrence through association of beclin-1 to bcl-2 and has poor effects on apoptosis as it decreases the activity of the pro-survival Erk-1/2, but increases the activity of the anti-apoptotic Akt. The subsequent addition of RAD potentiates the pro-apoptotic effects of CLC as it enhances the inhibition of Erk-1/2 and inhibits, at downstream levels, the Akt-dependent signalling (activated by CLC). In this way, the sequential treatment with the two agents induces a potent switch from autophagy to apoptosis in EPCs.