Figure 7. Crystal structure of the Kir3.2 E236R mutant.
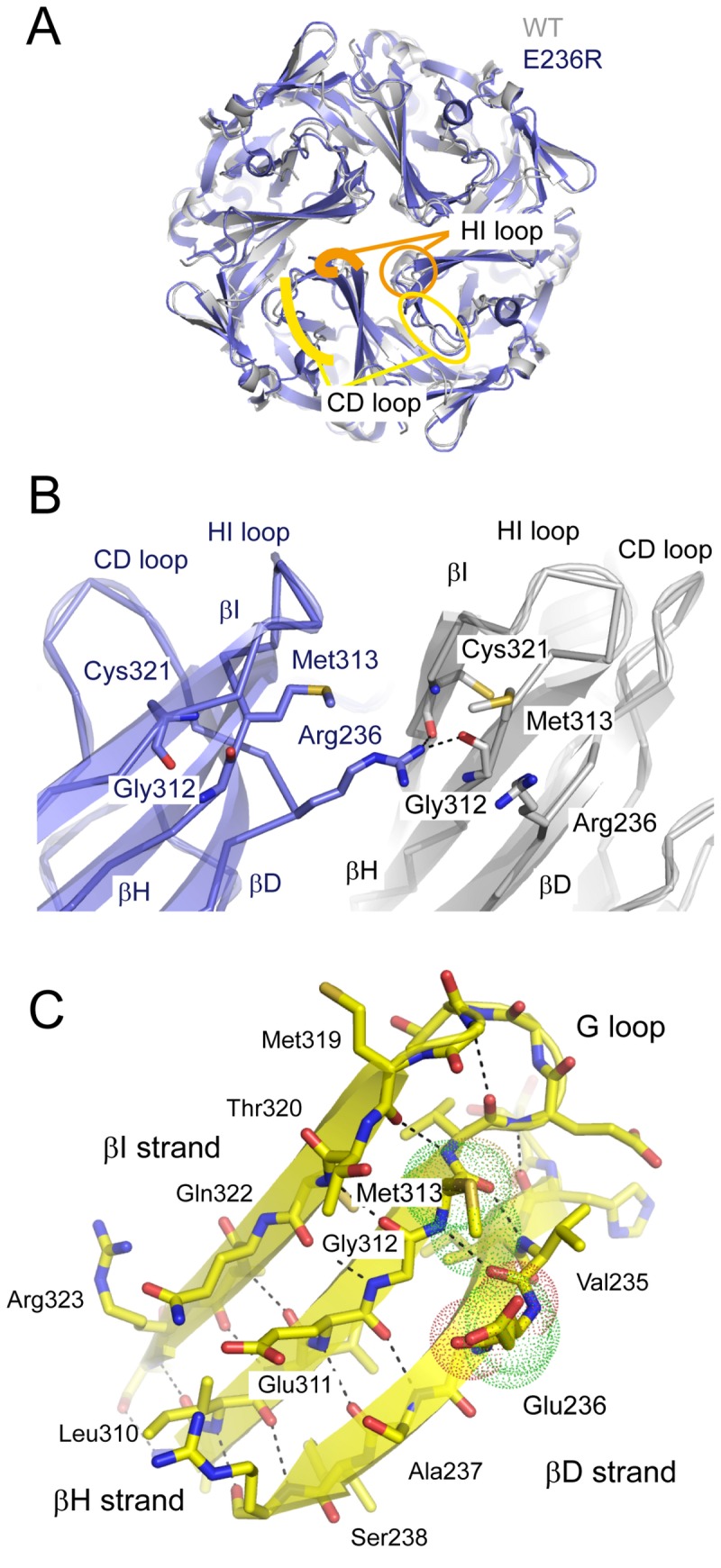
A. Comparison of the crystal structures of the cytoplasmic domains (CPDs) of WT and E236R channels. The CPD of the E236R mutant (blue) behaves as a tetramer and has a structure similar to that of the WT in a closed conformation (gray). The βC and βD strands (CD loop; yellow) and HI loop (orange) are denoted by circles in 1 subunit and traced with lines in the next subunit.
B. Enlarged view of the subunit interface at position 236. An arginine introduced at site 236 of one subunit (blue) forms hydrogen bonds with the carbonyl oxygen atoms of Gly312 on the βH strand and Cys321 on the βI strand of the adjacent subunit (gray). The residues crucial for the interaction are shown as sticks.
C. The β-bulge in the βD strand. The β sheet observed from the pore is shown with ribbons and sticks. The side chains of Glu236 and Met313 are shown with dots. The β-type hydrogen bonds are disconnected between Glu236 and Gly237 on the βD strand and Gly312 on βH strand. The dashed line indicates the hydrogen bond between the main chain atoms.
