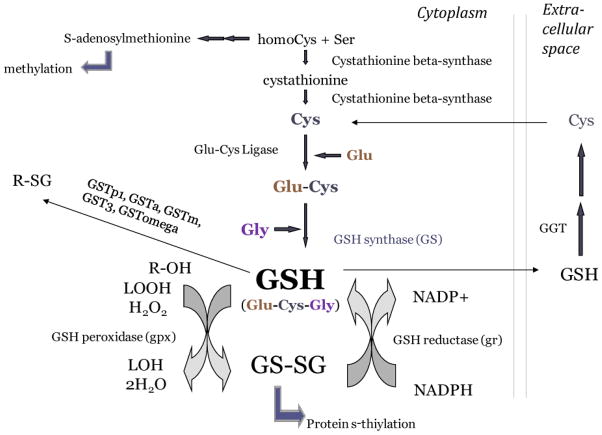
Figure 1. Diagram of the glutathione redox system.
Glutathione is a tripeptide of cysteine, glutamate, and glycine, which undergoes oxidation and forms a homodimer GSSG. GSSG can participate in post-translation modification of proteins by s-thiylation. GSSG can also be recycled back to reduced glutathione by GSH reductase in a reaction which utilizes NADPH. GSH can also be shuttled to the extracellular space and utilized, after which its cysteine component can be recycled by gamma glutamyl transferase (GGT). The synthesis of glutathione draws from cysteine pools synthesized from cystathionine, which is made from homocysteine. Glutathione thus draws from the same source of homocysteine that is necessary to maintain levels of s-adenosylmethionine needed for DNA methylation and epigenetic gene control, which is especially relevant during embryonic development.