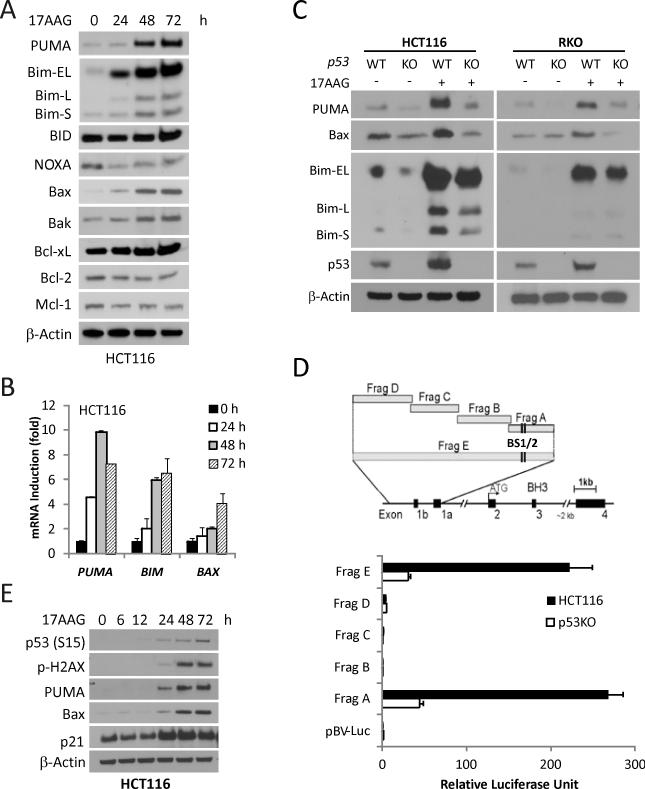
Figure 1. p53-dependent PUMA and Bax induction by 17AAG in colon cancer cells.
Indicated cells were treated with 1 μM 17AAG and analyzed for protein or mRNA expression at indicated times. (A) The expression of Bcl-2 family members was analyzed by Western blotting. β-Actin was used as a loading control. (B) mRNA Levels of PUMA, BIM, BAX were analyzed by real-time reverse transcriptase (RT) PCR. β-Actin was used as a control. (C) WT and p53-KO HCT116 and RKO cells were treated with 1 μM 17AAG for 48 h. PUMA, Bim, Bax and p53 expression was analyzed by Western blotting. (D) Top, schematic representation of the genomic structure of PUMA, highlighting the PUMA promoter fragments A--E used in the luciferase experiment. Two p53 binding sites (BS1/2) are indicated by vertical lines. Bottom, WT and p53-KO HCT116 cells were transfected overnight with a luciferase reporter plasmids and then treated with 1 μM 17AAG for 24 h. Reporter activities were measured by luciferase assay. The ratios of normalized relative luciferase activities (to the empty vector pBV-Luc as 1) were plotted. (E) The indicated proteins were analyzed by Western blotting.