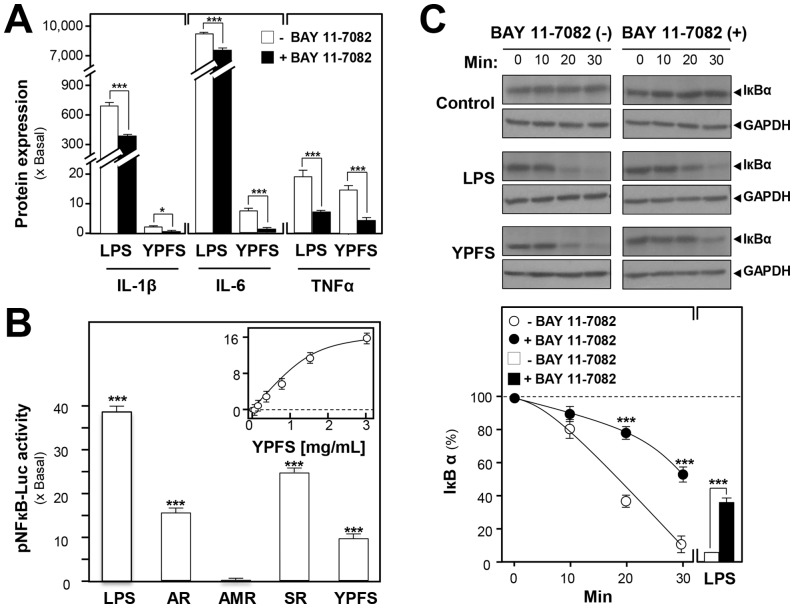
Figure 5. YPFS induces expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines via activation of NF-κB by enhancing the degradation of IκBα in cultured macrophages.
(A): Effects of BAY 11-7082 on protein expressions of pro-inflammatory cytokines inducing by YPFS in cultured macrophages. Macrophages were treated with herbal extracts for 24 hours in the present or absent of a specific NF-κB inhibitor BAY 11-7082 (5 µM). The cultured medium was collected to analyze the protein expressions of pro-inflammatory cytokines using multiplexed bead-based immunoassay. (B): The induction of pNF-κB-Luc by the extracts of AR, AMR, SR and YPFS in cultured macrophages. A luciferase-reporter containing five NF-κBs and a down-stream luciferase reporter gene, namely as pNF-κB-Luc, was used in the transfected macrophages. Cultured macrophages, transfected with pNF-κB-Luc, were treated with the herbal extracts for 24 hours. LPS (1 µg/mL) was used as a positive control. The cell lysates were subjected to luciferase assay to measure the transcriptional activity driven by NF-κB. (C): Effects of BAY 11-7082 on YPFS-induced degradation of IκBα in cultured macrophages. Cultures were incubated with BAY 11-7082 for 3 hours prior to stimulation with 3 mg/mL YPFS for the indicated times. Cell lysates were analyzed by western blot using indicated antibody for IκBα and GAPDH. Values are expressed as the fold of increase to basal reading (untreated cultures), and in Mean ± SD, where n = 4, each with triplicate samples.