Fig. 2. Dynamics of talin and Gα13 binding to β3 and the role of talin in integrin signaling.
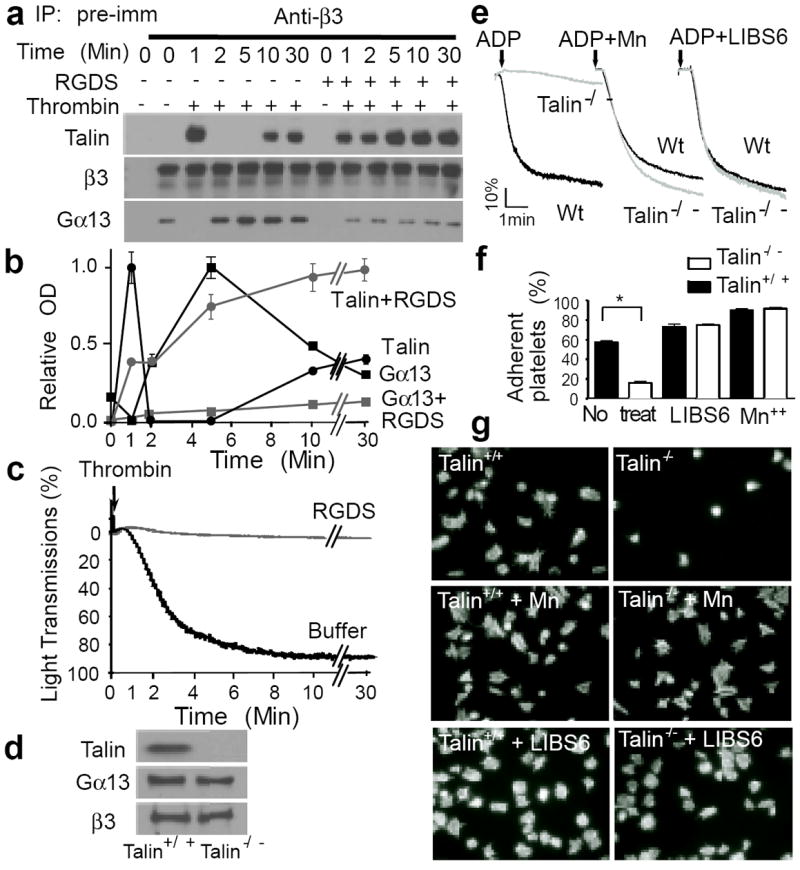
(a, b and c) Human platelets were stimulated with 0.025 U/ml α-thrombin (in an aggregometer) with or without 2 mM integrin inhibitor RGDS, solubilized at various time points, immunoprecipitated with anti-β3 or pre-immune rabbit serum, and immunoblotted for Gα13, talin, and β3 (additional controls in E.D. Fig 3d). (a) Typical immunoblots. (b) Quantification of immunoblots (mean ± SD, 3 experiments). (c) Turbidity changes indicating integrin-dependent platelet aggregation. (d) Immunoblotting of talin-1 in Wt and talin-1-/- mouse platelets. (e) Aggregation of Wt and talin-1-/- platelets stimulated with 5 μM ADP in the presence of 20μg/ml fibrinogen, with or without 1 mM MnCl2 or 0.3μg/ml LIBS6. (f) Adhesion of unstimulated mouse platelets to immobilized fibrinogen for 1 hour, with or without 1 mM MnCl2 or 0.18μg/ml LIBS6 (quantified as percentage of loaded platelets, mean ± SD, n=4, *p<0.001). (g) Images of phalloidin-stained mouse platelets spreading on fibrinogen for 1 hour, with or without 1 mM MnCl2 or 0.18μg/ml LIBS6 (quantification in E.D. Fig 4e).
