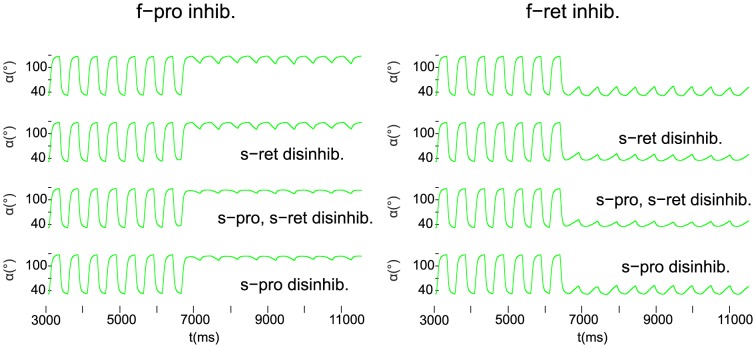
Figure 6. Selective inhibition of the fast motoneurons.
Left column: only the fast protractor motoneuron is inhibited. Right column: only the fast retractor motoneuron is inhibited. In both columns: top panel: normal disinhibition of both slow motoneurons (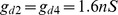 ); 2nd panel: strong disinhibition of the slow retractor motoneuron, only (
); 2nd panel: strong disinhibition of the slow retractor motoneuron, only (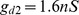 ,
, 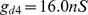 ); 3rd panel: strong disinhibition of both slow motoneurons (
); 3rd panel: strong disinhibition of both slow motoneurons (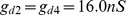 ); bottom panel: strong disinhibition of the slow protractor motoneuron, only (
); bottom panel: strong disinhibition of the slow protractor motoneuron, only (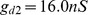 ,
, 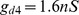 ). Note that the small-amplitude oscillation due to the activity of the slow motoneurons is positioned close to the extremal angle corresponding to the uninhibited fast motoneuron, e.g. to the maximal retraction position if only the fast retractor motoneuron remains active (left column).
). Note that the small-amplitude oscillation due to the activity of the slow motoneurons is positioned close to the extremal angle corresponding to the uninhibited fast motoneuron, e.g. to the maximal retraction position if only the fast retractor motoneuron remains active (left column).