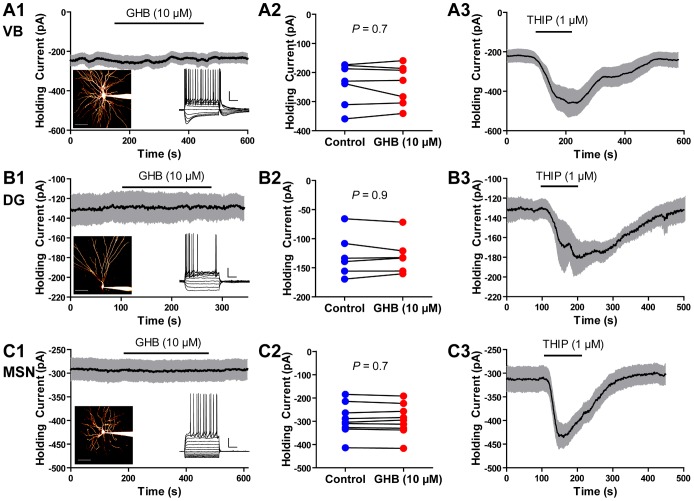
Figure 1. GHB has no effect on the holding current of voltage clamped neurons.
A1, Mean holding current over time in response to the application of GHB in VB thalamic neurons (n = 6). Grey area shows SEM. Left inset, representative image of a VB neuron. Scale bar 50 µm. Right inset, voltage response of a representative VB neuron to current injection. Scale bar 20 mV 200 ms. A2, Group results showing the mean holding current before and after GHB. A3, The δ-selective GABAA agonist THIP induced a significant inward current (control: −221±33 pA, THIP: −508±53 pA, n = 6, P = 0.0007). B1, Mean holding current over time in response to the application of GHB in dentate gyrus (DG) granule cell (n = 6). Grey area shows SEM. Left inset, representative image of a dentate gyrus granule cell. Scale bar 50 µm. Right inset, voltage response of a representative dentate gyrus granule cell to current injection. Scale bar 20 mV 200 ms. B2, Group results showing the mean holding current before and after GHB. B3, THIP induced a significant inward current (control: −131±10 pA THIP: −211±22 pA, n = 7, P = 0.01). C1, Mean holding current over time in response to the application of GHB in striatal medium spiny neurons (MSN) (n = 9). Grey area shows SEM. Left inset, representative image of a medium spiny neuron. Scale bar 50 µm. Right inset, voltage response of a representative medium spiny neuron to current injection. Scale bar 20 mV 200 ms. C2, Group results showing the mean holding current before and after GHB. C3, THIP induced a significant inward current (control: −314±26 pA THIP: −457±26 pA, n = 10, P<0.0001).