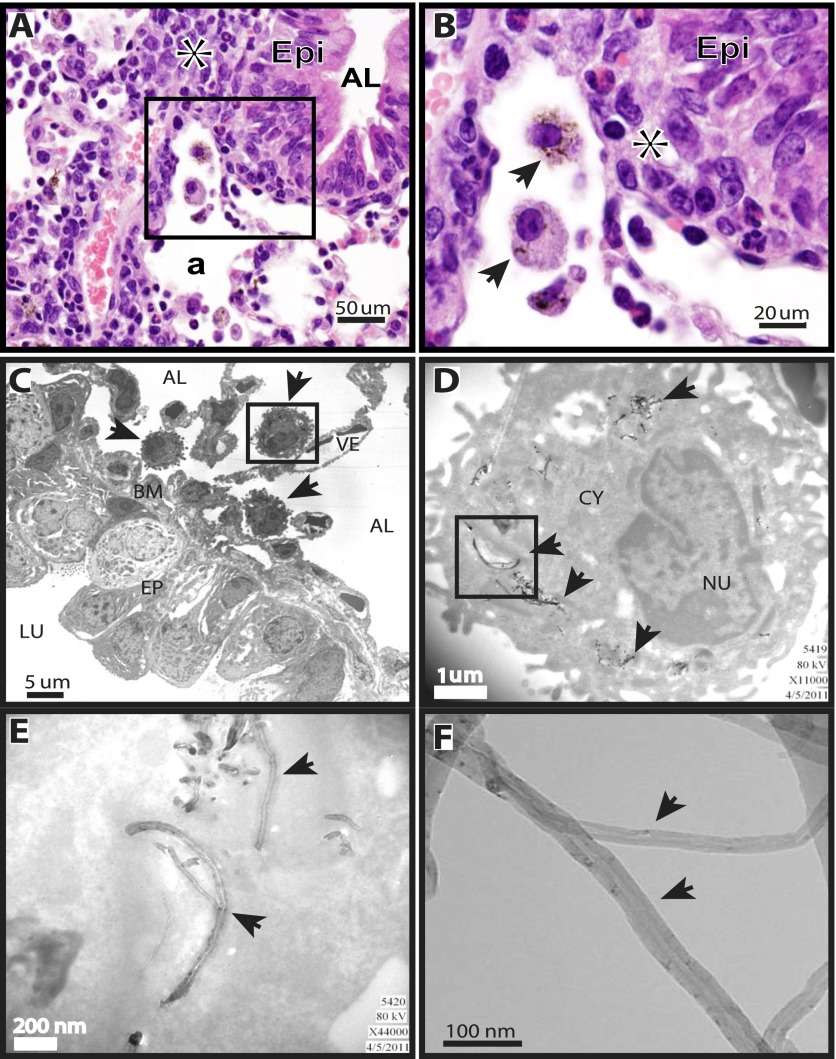
Figure 1.
Localization of multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) in mouse lungs, 1 day after oropharyngeal aspiration. (A) Photomicrograph at ×40 magnification of hematoxylin and eosin–stained lung section from a wild-type (WT) mouse shows alveolar macrophages containing MWCNTs. Asterisk indicates inflammation. Epi, epithelium; AL, airway lumen; a, alveolar region. (B) Higher magnification (×100) of inset from ×40 photomicrograph in A. Asterisk indicates inflammation. Arrows in ×100 photomicrograph indicate alveolar macrophages containing MWCNTs. Epi, epithelium. (C) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) shows localization of alveolar macrophages containing MWCNTs (arrows) adjacent to the airway basement membrane (BM). The macrophage enclosed by the inset box frame is shown at a higher magnification in D. AL, alveolus; LU, airway lumen; VE, blood vessel; EP, airway epithelium. (D) MWCNTs within a macrophage are indicated by arrows. Inset box frame is shown at a higher magnification in E. CY, cytoplasm; NU, nucleus. (E) MWCNTs within the cytoplasm of a macrophage (arrows). (F) Arrows indicate MWCNTs visualized by high-resolution TEM before delivery to mice.