Figure 2.
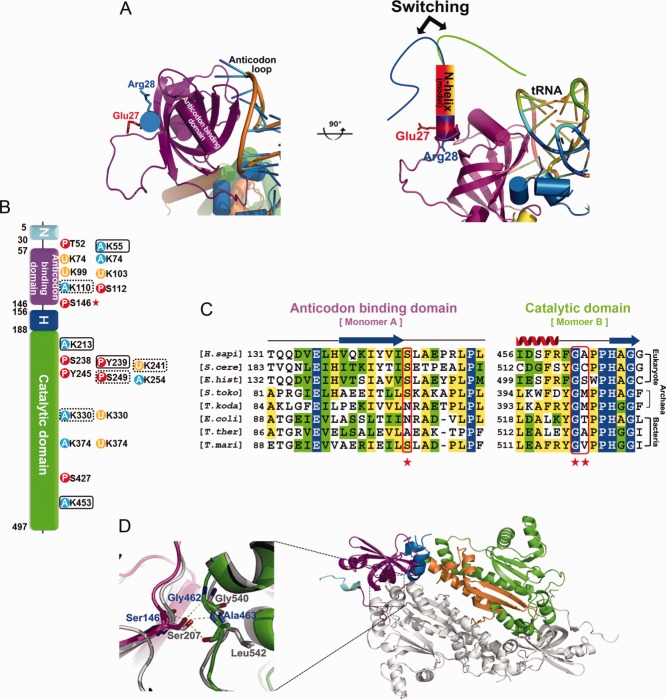
N-terminal extension, PTM, and key intermolecular interaction of DRS. (A) The switching model of the N-helix with our DRS structure. (B) PTM analyses. Acetylation, phosphorylation, and ubiquitination sites are shown as blue, red, and yellow circles, respectively. PTM sites uniquely observed in this study and residues observed both in the database and in our study are surrounded by black boxes and dotted boxes, respectively. Ser146, which is expected to play a key role in the organization of DRS, is marked with a red asterisk. (C) Sequence alignment of the interface residues of anticodon-binding domain and catalytic domain of DRSs from various organisms. Ser146, Gly462, and Ala463 of human DRS are marked with red asterisks. (D) Close-up view of Ser146 and the intermolecular interaction of DRS dimer. The structure of human DRS is superimposed with that of human KRS shown in a gray cartoon model.