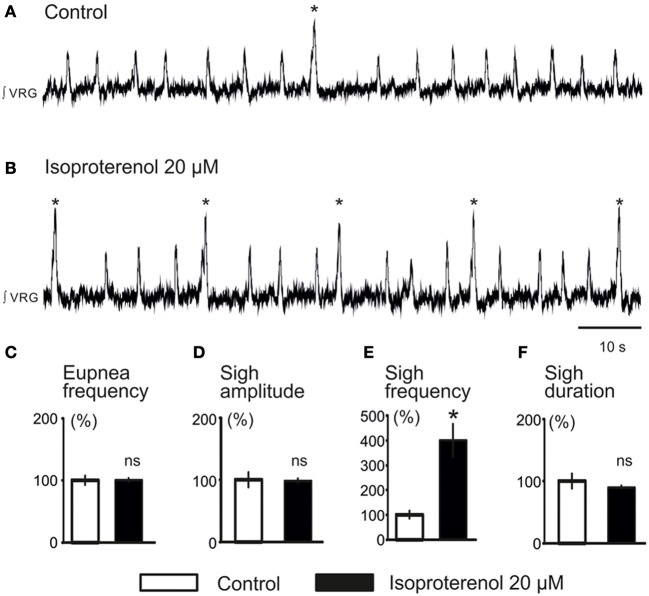
Figure 4.
Activation of β-NR modulates fictive sigh. (A) ∫VRG activity recorded from a slice under control conditions. (B) Isoproterenol 20 μM (β-NR agonist) activates β-NR and increases specifically the frequency of sigh activity. (C–F) Histograms show the effects of isoproterenol on sigh burst frequency (E) without affecting respiratory activity (C), sigh burst amplitude (D), or the sigh burst area (F) (*p < 0.05, n = 10).