Figure 2.
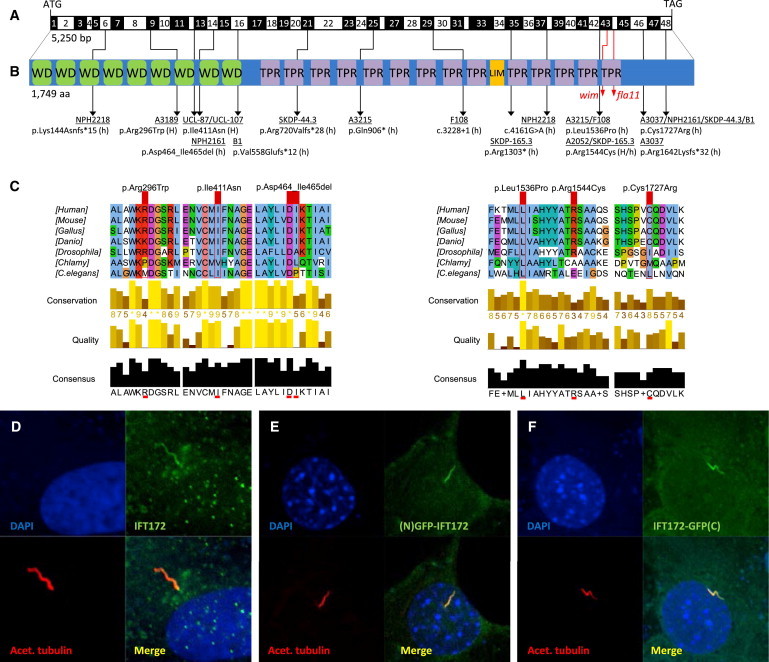
Biallelic IFT172 Mutations, Deduced Impact at Protein Level, and Subcellular Localization of WT IFT172
(A) Exon structure of human IFT172 cDNA. The positions of the start codon (ATG) and stop codon (TGA) are indicated.
(B) Domain structure of IFT172, which contains 9 WD-40 repeats (WD), located N-terminal to 14 tetratricopeptide repeats (TPR) and 1 LIM domain. For the mutations detected, black arrows indicate positions in relation to exons and protein domains. Family numbers are underlined. Abbreviations are as follows: H, homozygous; and h, heterozygous. IFT172 animal mutants wim (mouse, p.Leu1564Pro) and fla11 (C. reinhardtii, p.Leu1615Pro) are indicated by red arrows. Note the proximity of the detected missense changes p.Leu1536Pro and p.Arg1544Cys to the wim locus at position Leu1564.
(C) A partial protein alignment of IFT172 shows evolutionary conservation of the identified missense changes (p.Arg296Trp, p.Ile411Asn, p.Leu1536Pro, p.Arg1544Cys, and p.Cys1727Arg).
(D) Antibody staining (polyclonal rabbit antibody, Abcam, 1:100) of WT IFT172 in human control fibroblasts shows axonemal and pericentriolar localization in comparison to acetylated tubulin (anti-acetylated alpha tubulin, mouse monoclonal antibody, Abcam, 1:1000).
(E and F) Localization of human WT IFT172 constructs, once with an N-terminal GFP tag (E) and once with a C-terminal GFP tag (F), after transfection of a 48 hr serum-starved NIH 3T3 cell line. Immunofluorescence on a confocal microscope (Zeiss, LSM 720) confirmed axonemal localization with enrichment at the ciliary base upon overexpression.
