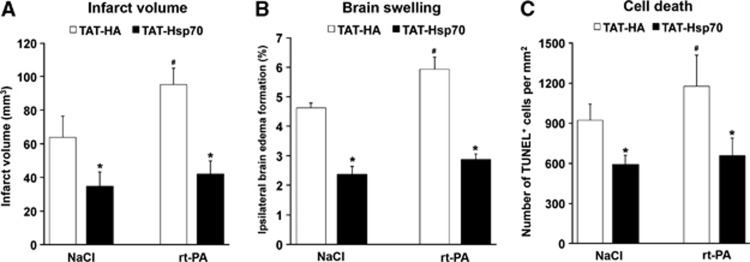
Figure 2.
TAT-heat-shock protein 70 (Hsp70) reduces rt-PA-mediated brain toxicity. Animals were intravenously treated with either rt-PA (10 mg/kg body weight (BW)) or NaCl (control) at the beginning of reperfusion followed by intravenous infusion of TAT-Hsp70 or TAT-HA 12 hours after stroke onset. (A) Analysis of infarct volumes on day 3 after induction of stroke using 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining (n=8 per condition). (B) Measurement of brain edema from mice used for (A) by subtracting the increase of ipsilateral hemispheric volume in comparison to the contralateral hemisphere. (C) Analysis of brain injury using TUNEL staining on day 3 poststroke. Animals (n=6 per condition) were treated as stated above. *Significantly different from controls, P<0.05. #Significantly different from mice treated with both NaCl and TAT-HA. TAT, transactivator of transcription; TUNEL, TdT-mediated dUTP nick end labeling.