Figure 3. In vivo depletion of bone marrow derived macrophage abrogates therapeutic benefit from combined NK+mAb9.2.27 treatment.
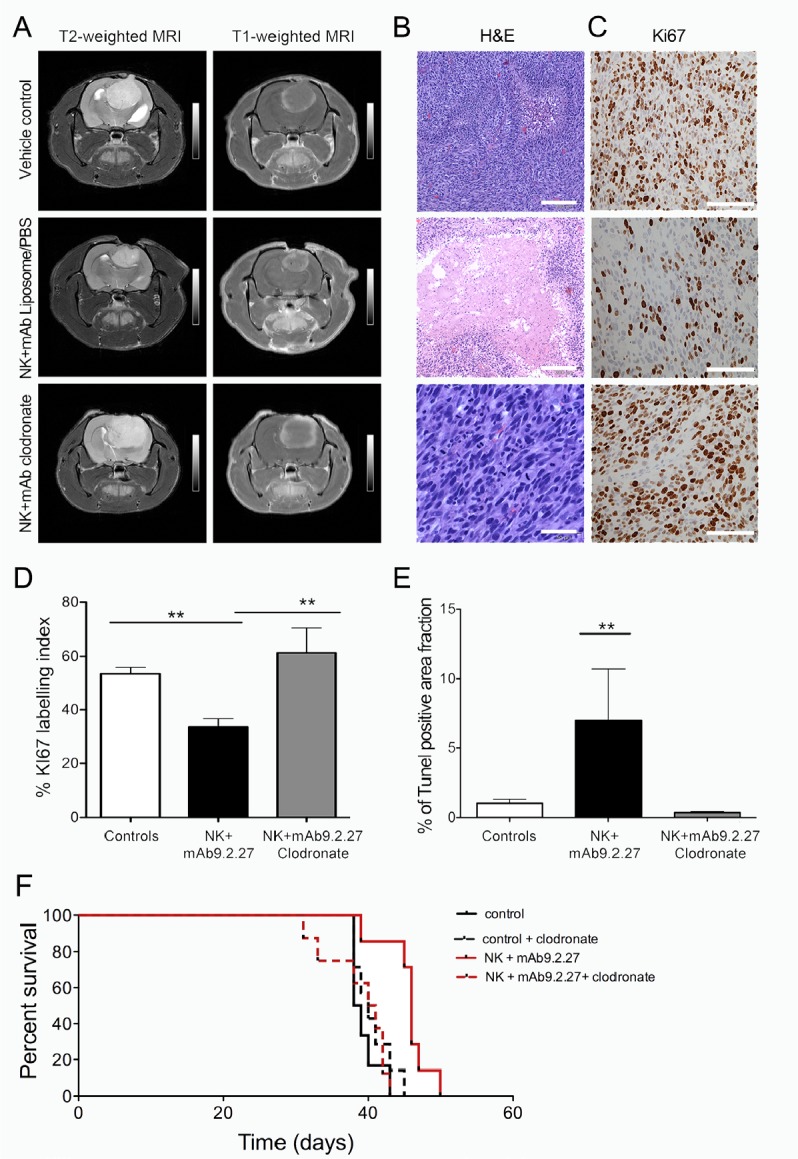
(A) Longitudinal axial post-contrast T1-weighted and T2-Weigted MRI images of nude rats bearing P3-30 tumors treated with combination NK+mAb9.2.27, vehicle (PBS/liposomes) control, and NK+mAb9.2.27 treated animals given weekly intraperitoneal clodronate encapsulated liposomes. (B) H&E of representative animals from the vehicle control, NK+mAb9.2.27 combination and NK+mAb9.2.27+clodronate (Scale bar 200 μm, Magnification 100 X). (C) Representative Ki67 labeling in vehicle control, NK+mAb9.2.27 combination and NK+mAb9.2.27+clodronate treated animals (Scale bar 100 μm, Magnification 200X). (D) % Ki67 labeling index and (E) quantification of area fraction TUNEL positive apoptotic/necrotic cells. Data in (D) and (E) represent mean ±SEM of all tumors in the groups, **p<0.01 and *p<0.05. (F) Kaplan –Meier survival curves of NK+mAb9.2.27 treated and control tumor with or without macrophage depletion by clodronate, showing surviving fraction, n=8 animals/group.
