Figure 5. IFN-γ and mAb9.2.27 increase cytotoxicity of microglia against GBM.
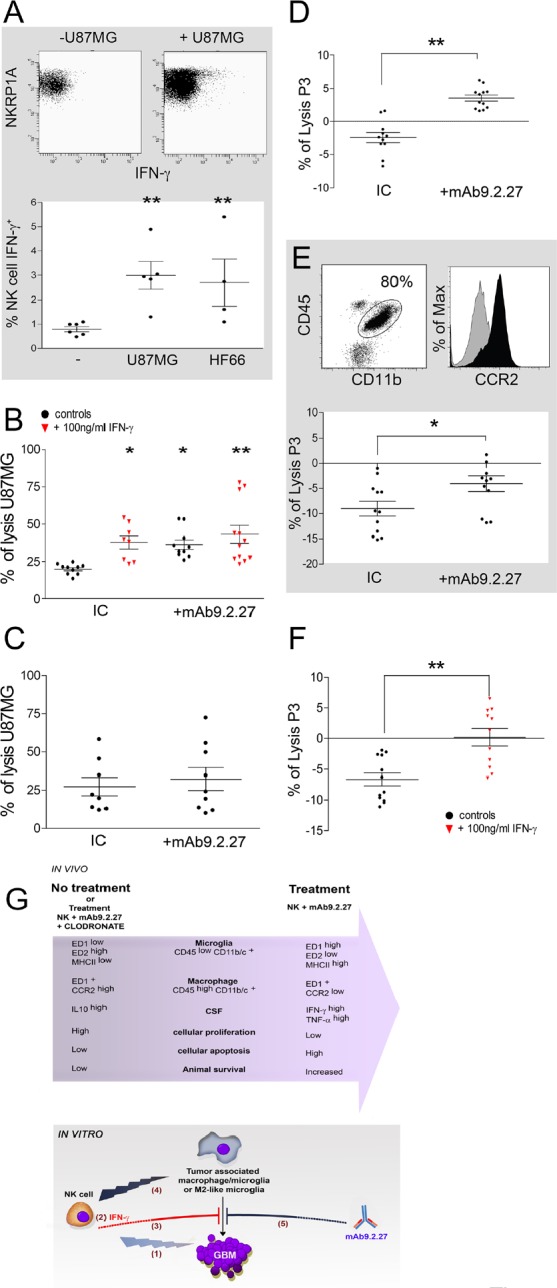
(A) Upper panel: dot plot showing IFN-γ secretion in IL-2 activated NK cells in contact with U87MG cells, Lower panel: quantification of IFN-γ secretion in IL-2 activated NK cells co-cultured with U87MG or HF66 at ratio 2/1 for 18 h. (B) % lysis of U87MG in vitro by microglia from naïve LEWIS rats following activation with IgG2a isotype control, IFN-γ or/and mAb9.2.27. (C) % lysis of U87MG in vitro by NK cells in the presence of IgG2a isotype control or mAb9.2.27. (D-E) Ex vivo purified rat (D) and patient (E) macrophage/microglia from tumor microenvironment were investigated for cytotoxicity against P3-30 tumor pre-incubated or not with mAb9.2.27. Human TAMs were phenotyped for CD45+CD11b+CCR2 expression (E dot plot: CD45+ against CD11b+. E Histogram: isotype control grey histogram, CCR2 black histogram). Lower panel: % lysis of P3-30 tumor by ex vivo TAM from patient GBM following activation with IgG2a isotype control, or mAb9.2.27. (F) Cytotoxicity of rat TAMs was also investigated after 96 h (F) incubation with 100 ng/ml of IFN-γ. Cell viability was determined by flow cytometry using TOPRO-3 as supravital dye. Data are plotted as mean ±SEM, **p<0.01, *p<0.05. (G) Adoptively transferred NK cells as initiators of GBM destruction: schematic representation of the in vivo and in vitro experimental findings.
In vivo: combination NK+mAb9.2.27 treatment leads to increased infiltration of the tumor by microglia and macrophages with pro-inflammatory phenotypes, with respectively ED1high ED2low MHC class IIhigh and ED1+ CCR2low molecular expression. This was associated with increase of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the CSF of NK+mAb9.2.27 treated animals, as well as diminution of cellular proliferation and increased tumor cell apoptosis. This resulted in increased animal survival that was abolished by depletion of systemic macrophages by injection of liposome-encapsulated clodronate.
In vitro: activated NK cells induced cellular cytotoxicity against GBM (1). The NK cells/GBM interaction led to IFN-γ secretion by NK cells (2). This cytokine inhibited tumor survival promoted by tumor-associated macrophages/microglia (3). NK cells efficiently killed anti-inflammatory M2-like microglia (4). Moreover, mAb9.2.27 inhibited tumor survival mediated by tumor associated macrophages/microglia (5).
