Fig. 3.
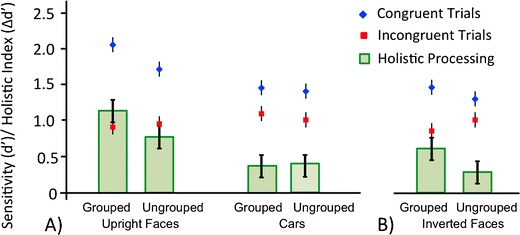
Sensitivity (d′) for the congruent (diamonds) and incongruent (squares) conditions, and the resulting index of holistic processing (filled bars, reflecting the difference between these conditions) for (a) upright faces and cars in Experiment 1 and (b) inverted faces in Experiment 2. Holistic processing was reduced (i.e., the congruency effect) for upright and inverted faces, but not for cars, when the stimuli were presented in the context of perceptual cues discouraging the grouping of the top and bottom parts. Error bars represent standard error values
