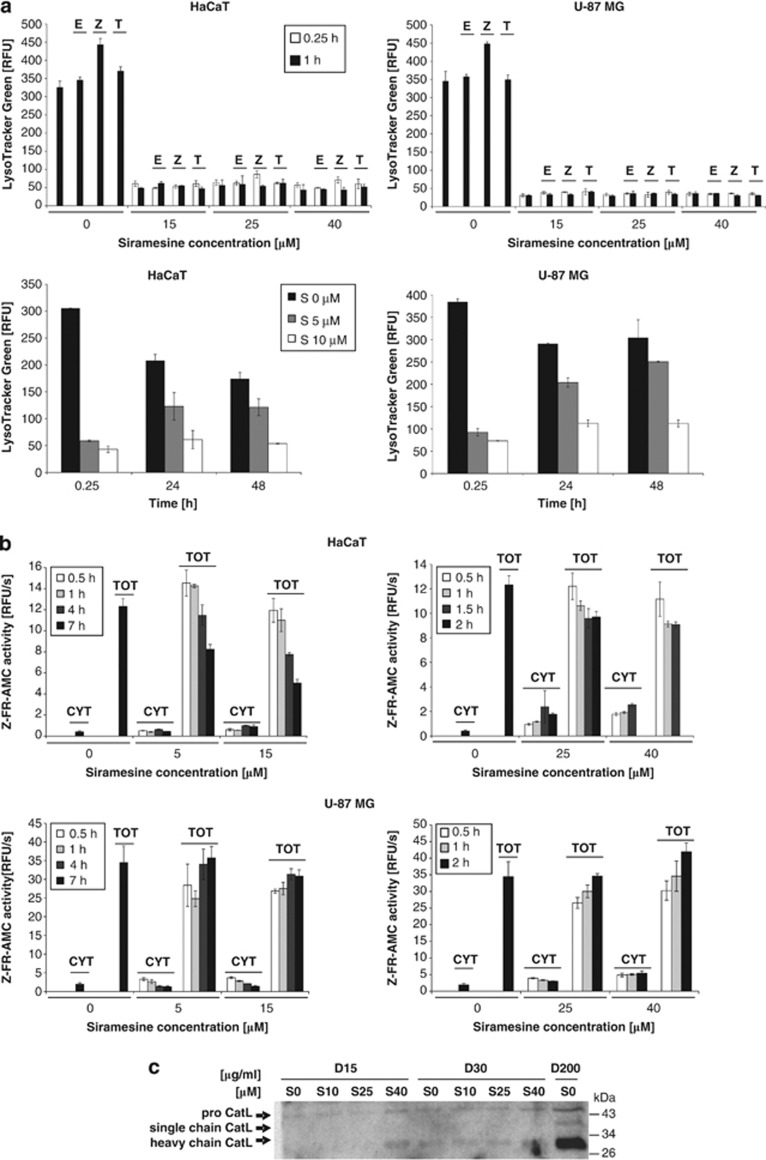
Figure 6.
Effect of siramesine on lysosomes. (a) The ability of lysosomes to accumulate LysoTracker Green after siramesine treatment. HaCaT and U-87MG cells were treated with different siramesine concentrations and incubated for the indicated time. Pancaspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK (20 μM), cathepsin inhibitor E-64d (10 μM) and the lipophilic antioxidant α-tocopherol (0.3 mM) were applied 2 h before siramesine treatment. After incubation with siramesine, all cells were stained at once with LysoTracker Green at a final concentration of 40 nM and analysed with a flow cytometer. The geometric mean of LysoTracker Green fluorescence intensity for each sample is displayed. The experiments were performed in duplicate; the bars represent mean±S.D. (b) Fluorimetric detection of cytosolic and total cysteine cathepsin activity after siramesine treatment based on Z-FR-AMC substrate hydrolysis. HaCaT and U-87MG cells growing in a 96-well plate were treated with different siramesine concentrations. After incubation with siramesine, 15 or 200 μg/ml digitonin was added directly to the wells to lyse only the plasma membrane (cytosolic activity) or all cell membranes (total activity), respectively. After 12 min incubation with digitonin on ice, the cysteine cathepsin activity was measured fluorimetrically using Z-FR-AMC, and the initial velocities of the reactions were calculated. The experiments were performed in triplicate; the bars represent mean±S.D. (c) Western blotting and immunodetection of cathepsin L in cytosolic and total extracts of HaCaT cells 1 h after siramesine treatment. Cytosolic and total extracts were prepared with 15 or 30, and 200 μg/ml of digitonin, respectively. Equal volumes of samples were loaded, proteins were resolved in 12.5% SDS-PAGE, transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane and labelled using specific antibodies. Z, Z-VAD-FMK; E, E-64d; T, α-tocopherol; S, siramesine; D, digitonin; CYT, cytosolic; TOT, total