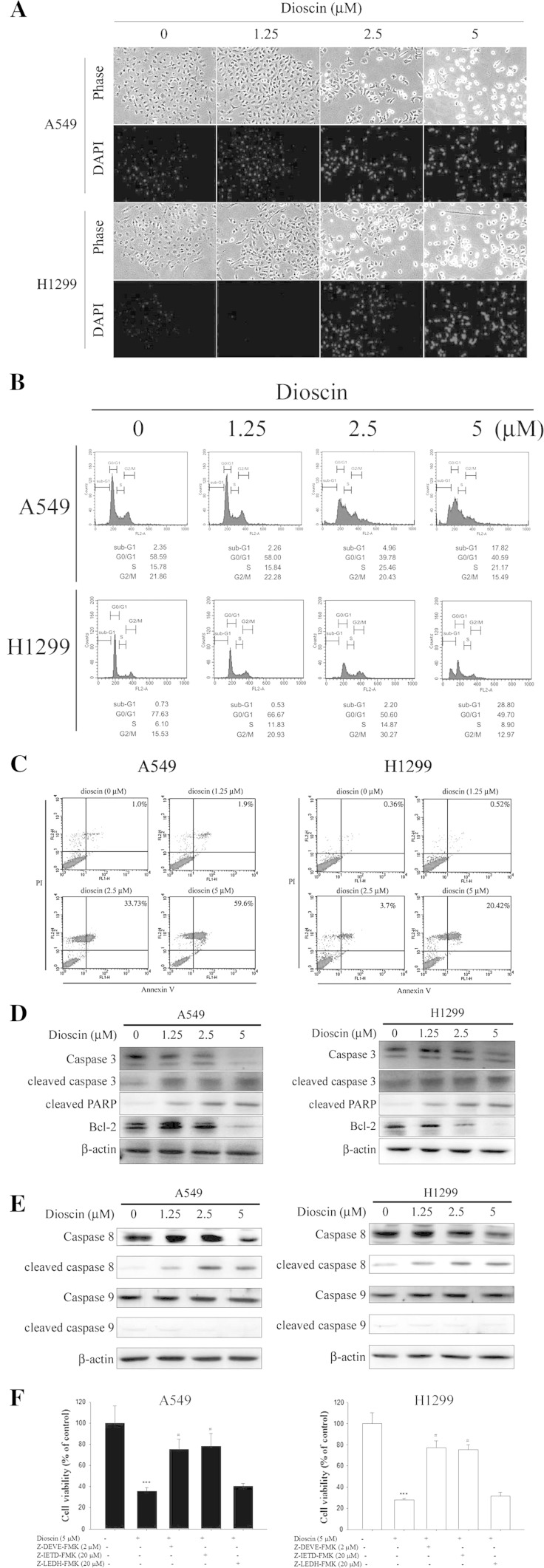
Fig. 2.
Dioscin-induced cell apoptosis in human lung cancer cell lines. a Cells were treated with different concentrations of dioscin (0–5 μM) for 24 h and then subjected to DAPI staining for DNA (blue areas) by fluorescence microscopy. b A549 and H1299 cells were incubated for 18 h in the absence of serum and then treated with indicated concentrations of dioscin for 24 h, after which the cells were stained with PI and analyzed for DNA content by flow cytometry. Furthermore, after being treated with different concentrations of dioscin for 24 h, cells were harvested and then subjected to quantitative analysis of cell apoptosis by annexin-V and PI double-stained flow cytometry (c), or subjected to Western blotting with an antibody against Bcl-2, PARP or caspase-3 antibody (d), as well as cleaved caspase-8 and caspase-9 (e). β-Actin acting as an internal control. f Cells were treated with 5 μM dioscin for 24 h in the presence or absence of 2 μM Z-DEVE-FMK, 20 μM Z-IETD-FMK and 20 μM Z-LEHD-FMK and then subjected to MTT assay to determine cell viability. Results are shown as mean ± SD. ***P < 0.001, control versus dioscin; #P < 0.05, dioscin versus Z-DEVE-FMK, Z-IETD-FMK and Z-LEHD-FMK plus dioscin