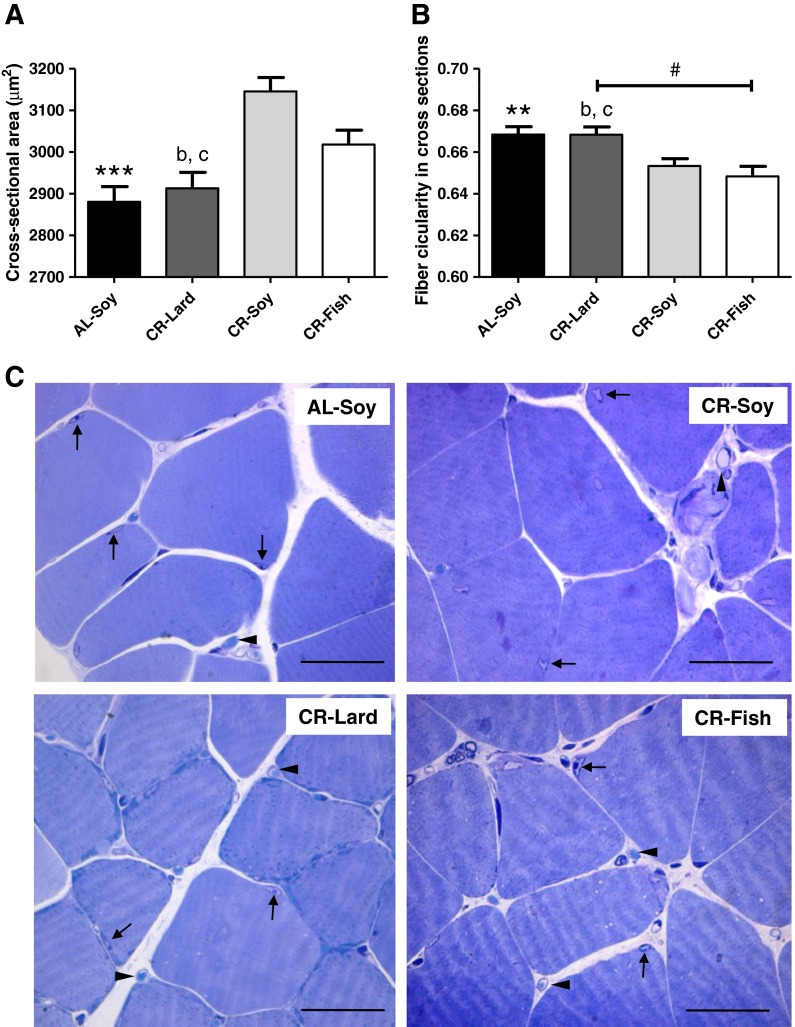
Fig. 1.
Structural changes of skeletal muscle fibers. a Calorie restriction increased fiber cross-sectional area in gastrocnemius (AL-Soy vs. CR-Soy, ***p < 0.001). Cross-sectional area was significantly lower in the CR-Lard group compared with both CR-Soy (b p < 0.001) and CR-Fish (c p < 0.001) groups. b Fiber circularity in cross-sectioned gastrocnemius muscle was decreased as a result of CR diet (AL-Soy vs. CR-Soy, **p < 0.01). Fibers from the CR-Lard group exhibited higher circularity than those from CR-Soy (b p < 0.01) and CR-Fish (c p < 0.001) groups. Additionally, a linear trend was observed as a function of dietary fat source (# p < 0.01). Between 1,000 and 1,400 fibers from five different animals were measured for calculating the cross-sectional area and circularity values. c Representative light microscopy images showing the gastrocnemius fibers from the four dietary groups. Fibers appear surrounded by connective tissues in which capillaries are frequently found (arrow heads). Arrows denote the presence of muscle fiber nuclei. Bars are equivalent to 50 μm