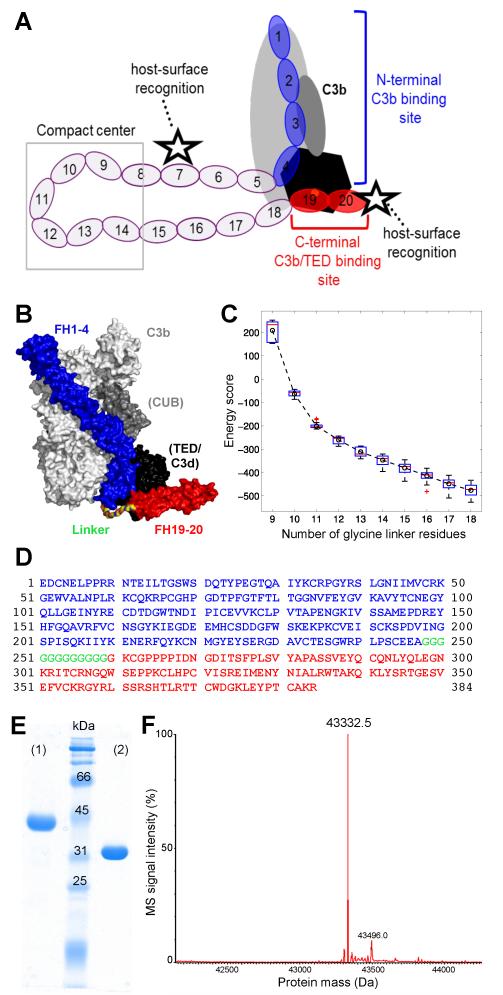
FIGURE 1.
Design and characterization of mini-FH. (A) Schematic representation of FH binding to complement opsonins (mainly C3b) and host surface markers. Whereas CCP domains 1-4 (blue) bind to C3b (grey/black) and exert regulatory activities, CCP19-20 (red) recognize polyanionic surface patches (star symbol) and binds to the TED domain (black) of C3b, iC3b and C3dg. (B) Superimposition of the co-crystal structures of C3b:FH1-4 (PDB 2WII) (24) and C3d:FH19-20 (PDB 3OXU) (14). A polyglycine linker (colored by element) combining the C-terminus of FH1-4 (blue) with the N-terminus of FH19-20 (red) was designed by molecular modeling. All residues are shown as surface representation. C3b is shown in light grey with the CUB and TED domains highlighted dark grey and black, respectively. C3d, which corresponds to TED, is also shown in black. (C) Energy score of modeled complexes versus number of glycine residues in the linker. The box plot shows the energy score distribution based on the top 80 models of each linker length. The circle and dashed line show the change of the average energy of these linkers. A linker length of 12 glycines was selected for this study. (D) Amino acid sequence of mini-FH with residues derived from FH1-4 construct and FH CCP19-20 marked in blue and red, respectively. The 12 residue long polyglycine linker is marked in green. Please note that the FH1-4 construct used in this study, and previously in the crystal structure of C3b:FH1-4 (24), contains an additional alanine residue following the native C-terminus (E264) of FH CCP4. Due to the alpha-mating secretion signal of the Pichia-expression vector and the restriction enzyme used for cloning, the secretion and cloning artifact EAEAAG precedes the FH-derived residues at the N-terminus accounting for the total theoretical mass of 43,333.7 Da. (E) Characterization of mini-FH by SDS-PAGE (12% gel, Coomassie staining). Mini-FH emerges as a single clean band at the expected size under both reducing (1) and non-reducing (2) conditions; faster mobility in (2) indicates presence of disulfide bonds. (F) Mass-spectrometric analysis of mini-FH. The deconvoluted mass spectrum shows one dominant peak at 43,332.5 Da, which is consistent with the theoretical mass mini-FH and attests identity and high purity of the preparation.