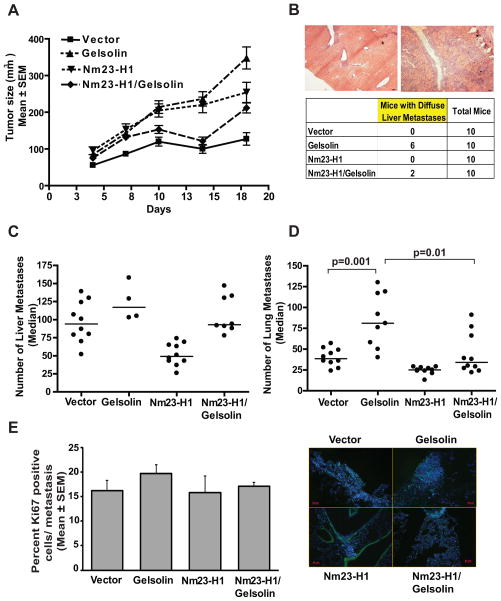
Figure 5. Nm23-H1 reduces the pro-metastatic effect of Gelsolin in a 4T1 spontaneous metastasis assay.
A. 5×105 4T1 cells expressing either vector, Flag-tagged Nm23-H1 (Nm23-H1), GFP-tagged Gelsolin (Gelsolin) or both proteins (Nm23-H1/Gelsolin) were implanted into the mammary fat pads of Balb/c mice. Primary tumor size through day 18 post-injection was determined, at which time tumors were removed. Difference in tumor growth was observed between the arms. B. Representative images (50X magnification) of discreet (right) and diffuse (left) liver metastases obtained from mice 10 weeks post-injection with 4T1 cells overexpressing Gelsolin. Scale bars = 100μm. Number of mice showing liver with diffuse metastases was reported in the table. C. Discreet liver metastases in each arm were reported as median values. A dot represents the number of liver metastases indentified in each mouse. Mice presenting diffuse liver metastases (see figure 5B) were excluded from this analysis. Comparison of Gelsolin and vector arms (p=0.18), vector and Nm23-H1 arms (p=0.0002). The Nm23-H1/Gelsolin arm was not significantly different from the vector. D. Lung metastases in each arm, reported as median values. While Gelsolin overexpression increased metastasis by 107%, Nm23-H1overexpression reduced it by 36% (p=0.001 and p=0.0015, respectively) compared to the vector arm. Nm23-H1/Gelsolin arm showed a metastasis formation similar to the vector and significantly decreased metastasis compared the Gelsolin arm (59%, p=0.01). E. Ki67 staining of lungs from 4T1 injected mice. Representative pictures are shown in the right panel. Scale bar=50μm. The graphs show the percentage of Ki67 positive cells in metastasis expressed as the mean ± SEM.