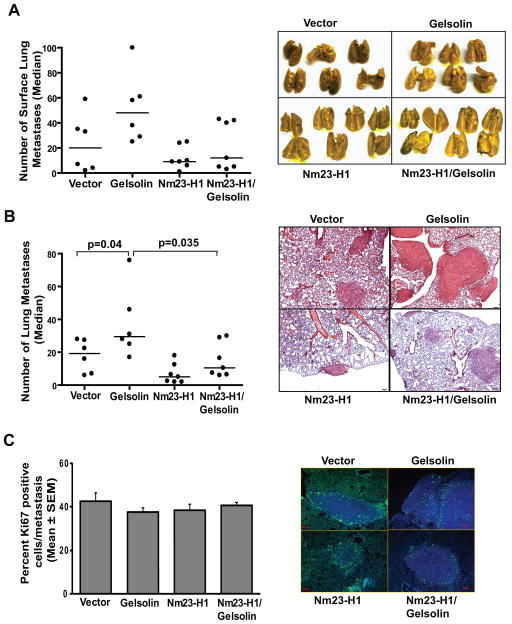
Figure 6. Nm23-H1 reduced the pro-metastatic effect of Gelsolin in an MDA-MB-231T experimental metastasis assay.
A. 5×105 MDA-MB-231T cells expressing either vector (n=6), Flag-tagged Nm23-H1 (Nm23-H1) (n=7), GFP-tagged Gelsolin (Gelsolin) (n=6) or both proteins (Nm23-H1/Gelsolin) (n=7) were injected into the tail veins of athymic nude mice. At 9 weeks post-injection, the mice were sacrificed and the lungs were collected and fixed in Bouin’s solution. Surface lung metastases were counted. The Nm23-H1/Gelsolin arm showed a 75% reduction in metastases as compared to the Gelsolin arm (p=0.101). B. H&E stained sections were evaluated for lung metastases. Each dot represents a single mouse. Gelsolin expression increased metastasis by 53.2% while Nm23-H1 reduced metastasis by 74.1%, the number of lung metastases compared to the vector arm (p=0.041 and p=0.035 respectively). Nm23-H1/Gelsolin arm showed a 65% reduction in metastases as compared to the Gelsolin arm (p=0. 035). C. Ki67 staining was performed on lungs from MDA-MB-231T injected mice. Representative pictures are shown in the right panel. Scale bar =50μm. The graph shows the percentage of Ki67 positive cells in metastasis expressed as the mean ± SEM.