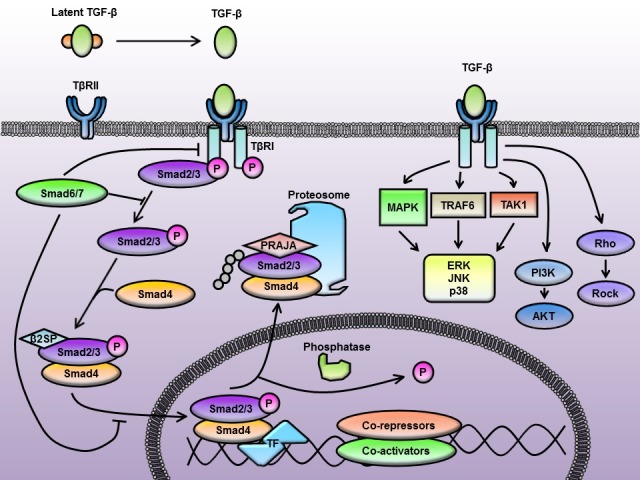
Fig. 1. TGF-β signaling through Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways. (A) Canonical pathway. TGF-β ligands activated TGF- βRI and TGF-βRII receptor complex recruits and phosphorylates the receptor specific Smad2/3. Hetero-oligomeric complex of Smad2/3- Smad4 translocates to the nucleus and binds to specific DNA sequence and interacts with transcription factors and cofactors to regulate transcription. The pathway is negatively regulated by the Smad6/7, which bind activated TGF-βRI, thereby preventing phosphorylation of Smad2/3, or recruit the E3 ubiquitine ligases to induce proteasomal degradation of the Smad2/3 (B) Noncanonical pathway. Smad-independent signaling. TGF-β can promote the activity of several signaling pathways other than Smad, including MAPKs, PI3K kinases, TRAF6- TAK1-p38/JNK, Rho-Rock, among others.