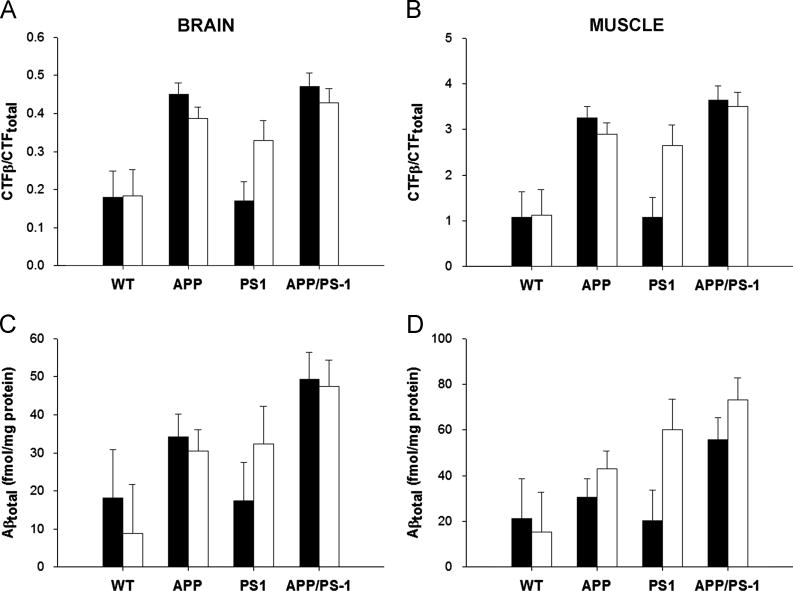
Figure 2. The Ketogenic Diet Did Not Reduce Aβ Levels in Brain or Skeletal Muscle.
The C-terminal fragment of APP (CTFβ; A–B) and Aβ (C–D) levels were measured by ELISA in brain (A, C) and skeletal muscle (B, D) of mice fed the control (filled bars) or ketogenic (open bars) diet. As expected, the presence of the APPΔNLh mutation significantly elevated both CTFs and Aβ over APP wild-type controls (p≤0.02). The ketogenic diet did not affect CTFβ or Aβ in either the brain or muscle when analyzed across all genotypes (p≥0.08). However, there was a modest decrease in CTFβ in both the muscle (p=0.07) and brain (p=0.05) of mice containing the APPΔNL mutation, indicating an interaction between diet and the APP genotype. There was no such interaction for Aβ (p≥0.67).