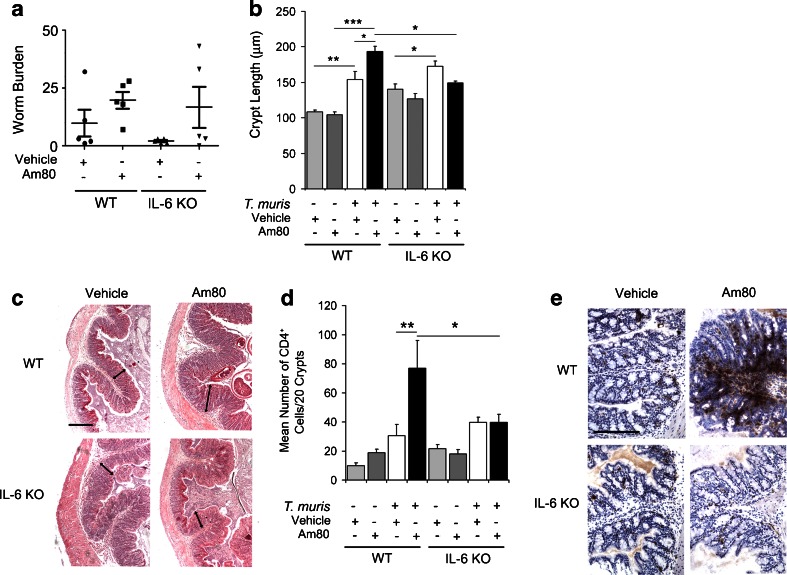
Fig. 1.
Activation of the retinoic acid receptor (RAR) increases pathology during T. muris infection but not in the absence of IL-6. a Wild-type or IL-6 KO mice were infected with 60 T. muris eggs to establish a chronic infection and treated with either vehicle or Am80. At day 35 p.i. worm burdens were determined. b Paraffin-embedded proximal colon sections were stained with haemotoxylin and eosin (H&E) and crypt lengths measured using Image J software. c Representative images of T. muris-infected proximal colon sections stained with H&E. The arrows demonstrate examples of the measurements which were taken. d Immunohistochemical staining of CD4+ cells was conducted on proximal colon sections from wild-type and IL-6 knock-out animals at day 35 p.i. Quantitative analysis of immunohistochemistry was carried out by counting the number of positively-stained CD4+ cells. e A representative image of each infected treatment group is shown, where positively stained cells are brown. Scale bars indicate 200 μm. Graphs show means + SEM (n = 5). Data are representative of two independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001