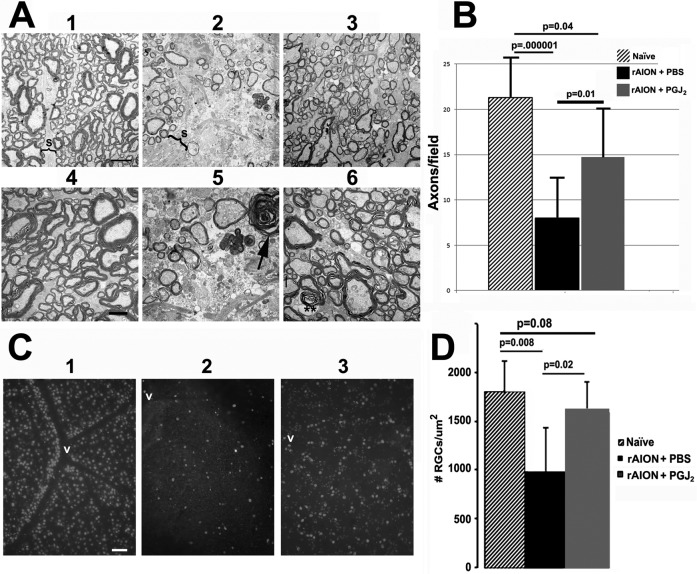
Figure 5.
Optic nerve and RGC stereological analysis of naive (no rAION, uninjected) eyes and in eyes after induction of rAION immediately followed by a single IVT injection of either PGJ2 or PBS. (A) TEM analysis: (1–3) are lower magnification (×2500); (4–6) are from the same general regions as seen in low power but at higher magnification (×4000). (1) Control ON: Axons (Ax) are relatively closely packed, with thin separating septae (S). (2) ON from an rAION-induced, PBS-injected eye. The septae (S) are greatly widened, with many fewer axons (Ax). (3) ON from an rAION-induced, PGJ2-injected eye shows axonal preservation. (4) Control ON: Normal myelinated axons in a näive (no rAION, uninjected) eye. (5) ON from an rAION-induced, PBS-injected eye. Compared with (4), the numbers of axons are greatly reduced, and there are degenerating axons showing demyelination (arrow). (6) ON from an rAION-induced, PGJ2-treated eye. Both large and small axons appear normally myelinated (double asterisks), and there are many more intact axons than in nerves from the eye injected with PBS (compare with [5]). Scale bars: 2 μm (A1–A3), 500 nm (A4–A6). (B) Axon quantification. Axons from 10 random fields were counted from micrographs obtained from lower-magnification TEMs. Mean ± SD of each group. The ONs from PGJ2-injected ONs at 30 days postinduction (gray bar) had more intact axons than ONs from PBS-injected eyes (black bar). Note the overlap of numbers of axons per field in PGJ2-injected eyes compared with naïve eyes. The number of axons in PGJ2-injected eyes compared with PBS-injected eyes was significant (2-tailed t-test, P ≤ 0.01). (C) Photomicrographs of representative retinal flat mounts of (1) naïve, (2) rAION-induced, PBS-injected, and (3) rAION-induced, PGJ2-injected eyes. RGCs are identified by Brn3a immunostaining. RGCs are more numerous near vessels (v) in the naïve eye. Scale bar: 50 μm. (D) Stereological analysis of Brn3a+ cells (RGCs) in naïve (no rAION, uninjected) eyes (hatched bar), rAION-induced, PBS-injected eyes (black bar), and rAION-induced, PGJ2-injected eyes (gray bar). Compared with naïve eyes, there was a significant loss of RGCs in rAION-induced eyes injected with PBS (P = 0.008), whereas eyes injected with PGJ2 immediately after induction of rAION showed a significant increase in the number of RGCs compared with PBS-injected eyes (P < 0.02).