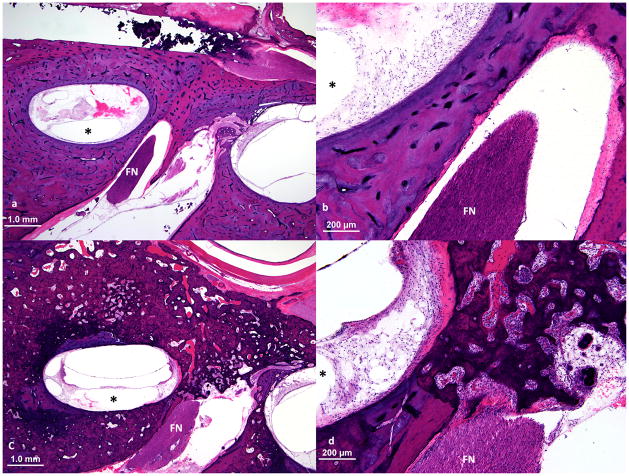
Figure 2.
Upper basal turn of cochlea and nearby facial nerve (FN) at the junction of the labyrinthine and the meatal segments of the facial nerve. a, b. Normal bone between upper basal turn of cochlea and the facial nerve. This patient (case 4) did not experience facial nerve stimulation. c, d. This patient (case 9) had facial nerve stimulation and showed full thickness involvement by otosclerosis of the bone between upper basal turn of cochlea and the facial nerve. Although the distance between the facial nerve and upper basal turn of the cochlea was similar to that in case 4, the normal bone was replaced by spongiotic bone with soft tissue deposition and neovascularization. (The electrode track is shown by an asterisk.)