Table 1. J-wave Syndromes: Similarities and Differences.
| J Wave Syndromes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inherited | Acquired | |||||
| ER in lateral leads ERS Type 1 |
ER in inferior or infero-lateral leads ERS Type 2 |
Global ER ERS Type 3 |
Brugada Syndrome |
Ischemia- mediated VT/VF |
Hypothermia- mediated VT/VF |
|
| Anatomic Location | Antero-lateral left ventricle |
Inferior left ventricle | Left and right ventricles |
Right ventricle | Left and right ventricles |
Left and right ventricles |
|
Leads Displaying J
point/ J-wave |
I, V4-V6 | II, III, aVF | Global | V1-V3 | Any of 12 leads | Any of 12 leads |
|
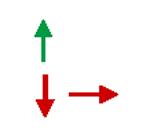
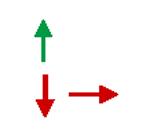
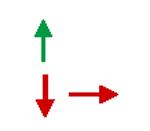
Response of J wave /ST
Elevation to: Bradycardia or pause Na+ channel blockers |
|
|
|

|
N/A N/A |
N/A N/A |
| Sex Dominance | Male | Male | Male | Male | Male71,72 | Either gender |
| VT/VF | Rare Common in healthy athletes12, 13, 34 |
Yes16,73 | Yes, Electrical storms17, 74 |
Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
Response of to
Quinidine: J wave /ST elevation VT/VF |

|

|

|

|
Limited data |
 75
75
|
|
Response of to
Isoproterenol: J wave /ST elevation VT/VF |

|

|
Limited data |

|
N/A | N/A |
ER= early repolarization; ERS=early repolarization syndrome; N/A=not available; VF=ventricular fibrillation; VT=ventricular tachycardia. Modified from 8, with permission.
