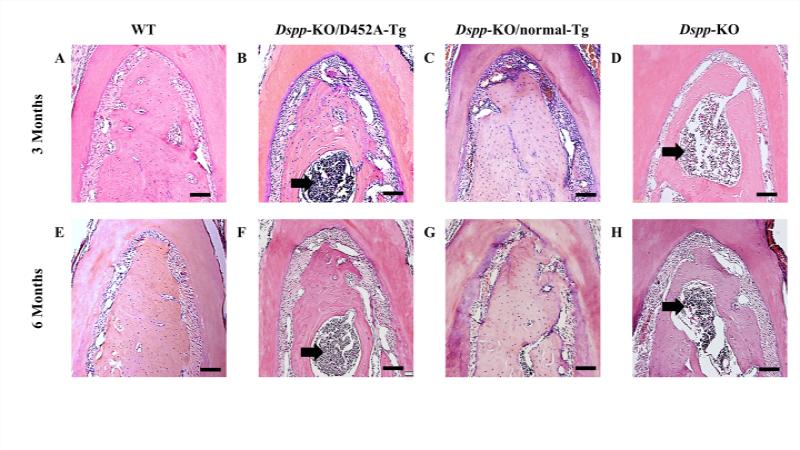
Figure 1. Failure to process DSPP into fragments leads to alveolar bone defects.
H&E staining of alveolar bone at both 3- and 6-months of age, showed that the Dspp-KO (D and H) and Dspp-KO/D452A-Tg mice (B and F) had significant alveolar bone loss in the furcation region of the first mandibular molar with inflammation (black arrows), compared to the WT mice (A and E). The transgenic expression of normal DSPP (C and G, Dspp-KO/normal-Tg mice) completely rescued the alveolar bone defects of Dspp-KO mice; the alveolar bone Dspp-KO/normal-Tg mice (C and G) appeared similar to those of the WT mice (A and E). Bar: 100 μm