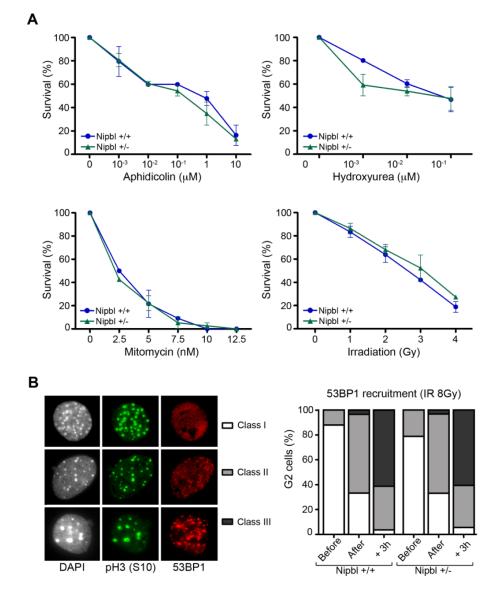
Figure 2. Nipbl deficiency does not increase DNA damage sensitivity in MEFs.
(A) Survival of wild-type and Nipbl heterozygous cells after exposure to the DNA damaging agents aphidicolin, hydroxyurea, mitomycin C and gamma irradiation at the indicated doses (n=2 clones per genotype). (B) Left: 53BP1 staining of G2 irradiated (8Gy) cells, identified as pH3(S10) positive, was categorized in three different classes: homogenous nuclear staining (class I), few foci with diffuse staining (class II) and many strong foci without diffuse staining (class III). Right: Quantification of these phenotypes before, immediately after and 3 hours after irradiation of wild-type and Nipbl heterozygous MEFs. (n ≥ 50 G2-cells per condition and per clone from two independent clones per genotype).