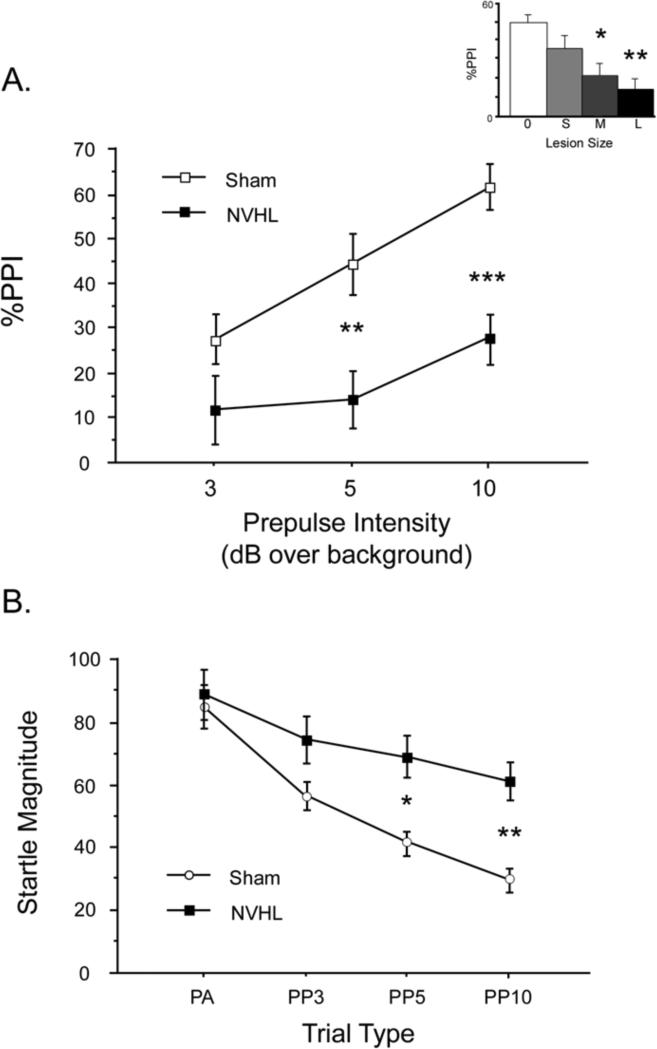
Figure 2.
NVHLs selectively disrupt sensorimotor gating of startle, and do not significantly alter levels of gene expression in the NAC or mPFC. A. PPI was significantly reduced in NVHL vs. Sham group rats. Main figure shows comparison of NVHL vs. Sham groups across 3 prepulse intensities; inset shows data collapsed across all prepulse intensities, but divided into 4 groups based on histological evidence of no VH damage (0) or small VH damage in Sham group rats (S), or medium (M) or large (L) lesions in NVHL group rats. * p < 0.035; ** p < 0.006; *** p < 0.001. B. Startle magnitude on pulse alone (PA) trials or on trials in which a pulse was preceded by prepulses of 3, 5 or 10 dB over background (PP3, PP5 or PP10, respectively). Elevated startle magnitude on prepulse trials in NVHL rats provides clear evidence of a reduced inhibitory impact of these weak sensory events on the motor reflex, i.e. reduced sensorimotor inhibition. * p <0.025; ** p < 0.006.